News / Blog
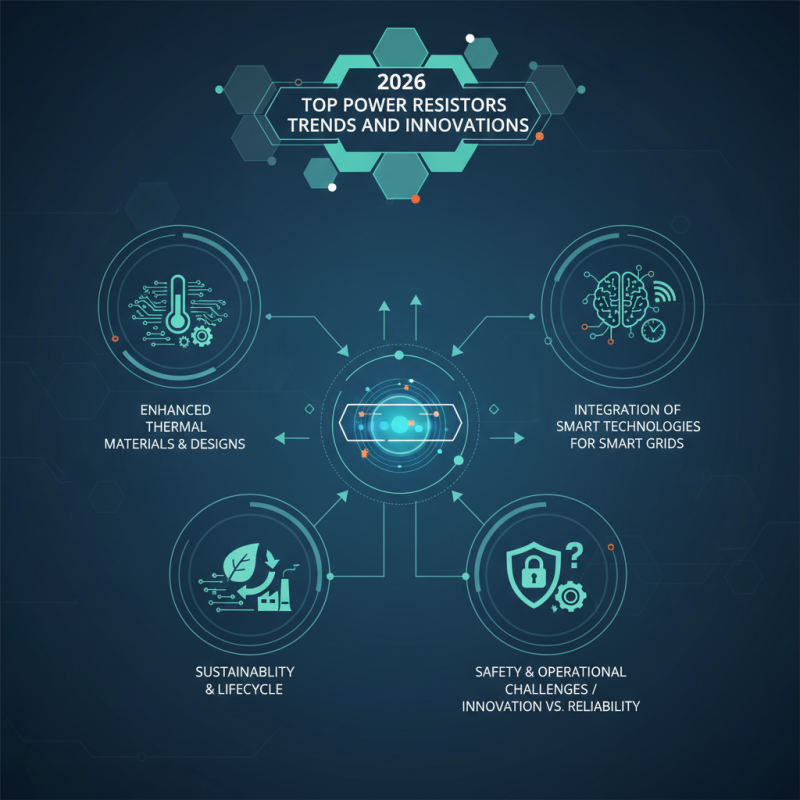
2026 Top Power Resistors Trends and Innovations to Watch?
The landscape of power resistors is evolving rapidly. As industries strive for improved efficiency and reliability, power resistors play a crucial role. Their applications span across automotive, telecommunications, and renewable energy sectors. Innovation within this field is not just welcome; it is essential.
In 2026, we will see trends that focus on enhanced thermal management. These advancements aim to improve the durability of power resistors. More robust materials and designs are emerging. This can lead to a noticeable increase in performance. However, it also raises questions about sustainability and the lifecycle of these components.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies is becoming common. Smart grids will rely heavily on advanced power resistors for real-time data. Yet, there's a delicate balance between innovation and reliability. As power resistors become more sophisticated, potential risks emerge. Companies must consider safety and operational challenges. The future holds promise, but reflection is key in navigating these innovations.
Emerging Materials in Power Resistor Technology for 2026
The landscape of power resistor technology is evolving rapidly. Emerging materials are shaping how these components perform in various applications. In 2026, expect to see a surge in the use of advanced ceramics and composite materials. These materials offer improved heat resistance and stability. They can withstand higher temperatures and deliver enhanced performance.
Opting for eco-friendly materials is becoming a priority. Manufacturers are exploring natural composites. These could reduce the environmental impact and provide better thermal management. Innovations like graphene and carbon nanotubes are intriguing. They promise high conductivity while being lightweight.
Tips: Consider how new materials can impact durability. Look for suppliers focusing on sustainable practices. Staying updated on material advancements is key. Explore case studies on the latest developments. Understanding how they affect design and application can save resources in the long run. The evolving trends hold potential, but challenges in implementation persist. Not every breakthrough will fit every application seamlessly.
Advancements in Thermal Management Solutions for Power Resistors
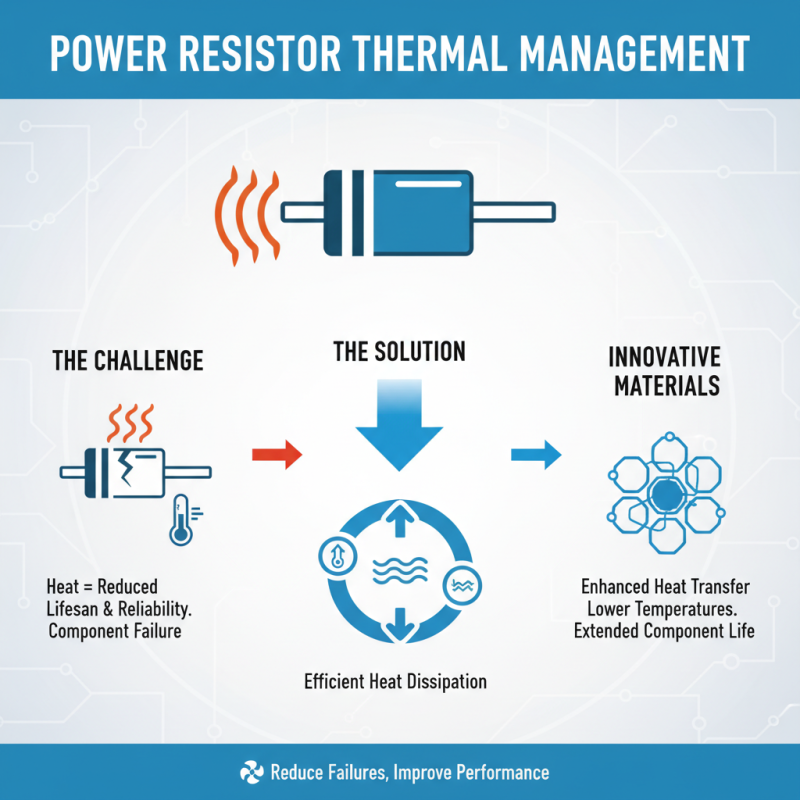
Thermal management is crucial for power resistors. Efficient heat dissipation can extend the lifespan and reliability of these components. Recently, innovative materials have emerged that enhance heat transfer. These materials help manage temperatures effectively, reducing failures.
Tips: Always consider the environment where power resistors operate. High ambient temperatures can lead to overheating. Effective thermal management solutions can mitigate this risk.
Active cooling methods, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, are gaining traction. While effective, they can add complexity to designs. Passive solutions like heat sinks are simpler but may not be enough in high-load scenarios. Finding the balance is vital for performance.
Tips: Regular checks on thermal performance can prevent unexpected issues. Keeping components clean and dust-free allows for better airflow and cooling efficiency. Remember, ignoring thermal management can lead to costly failures.
Smart Power Resistors: Integration with IoT and Digital Technologies
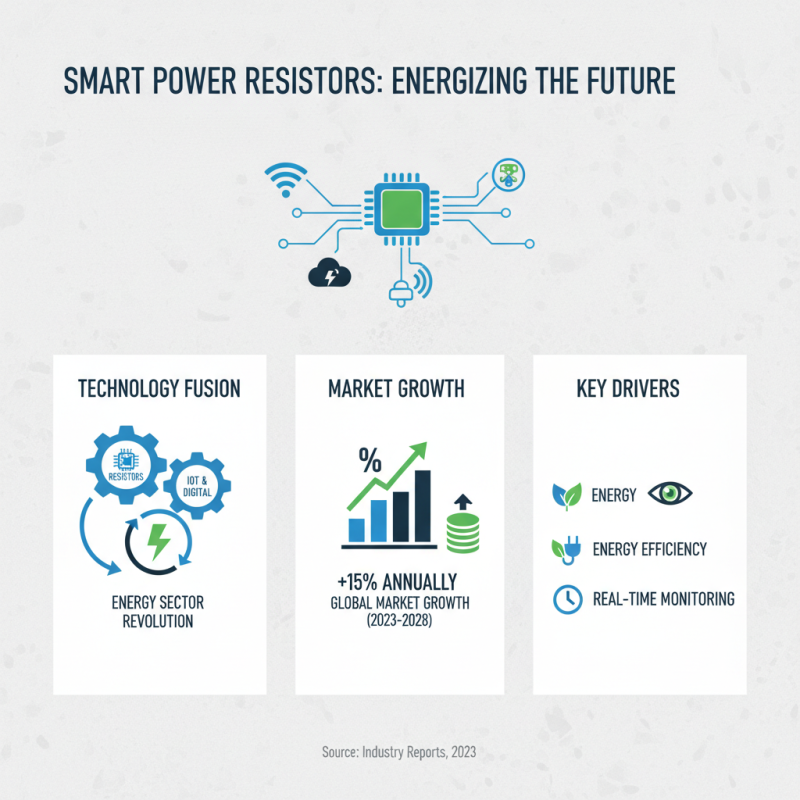
The integration of smart power resistors with IoT and digital technologies is revolutionizing the energy sector. Recent reports indicate that the global smart resistor market is projected to grow by over 15% annually between 2023 and 2028. This rise is largely due to the increasing demand for energy efficiency and real-time monitoring in various applications.
Smart power resistors enable better energy management and performance optimization. For instance, they can dynamically adjust their resistance based on environmental conditions and system demands. With sensors and connectivity features, these resistors can provide insights into energy consumption patterns. This data allows for timely adjustments, enhancing the longevity of systems.
However, the transition to fully integrated smart resistors isn't without challenges. Security concerns arise with greater connectivity. The complexity of installation and potential interoperability issues must be addressed. As companies move towards digital solutions, assessing risks while adopting innovations is crucial for sustainable development.
Sustainability Practices in the Manufacturing of Power Resistors
Sustainability is a growing concern in the manufacturing of power resistors. Data shows that over 40% of global energy consumption comes from industrial processes. This has led to increased pressure for manufacturers to adopt greener practices. Many companies are now shifting to eco-friendly materials. For instance, using recycled metals in resistor production is gaining momentum.
The manufacturing process itself needs improvement. A recent study highlighted that up to 25% of raw materials end up as waste. This not only harms the environment but also affects profit margins. Companies are exploring lean manufacturing techniques. These methods can reduce waste and enhance efficiency. Renewable energy sources are making their way into production facilities. Reports indicate that firms using solar or wind power decrease their carbon footprints significantly.
However, challenges remain. Implementing sustainability measures often requires upfront investment. Smaller manufacturers may struggle with funding. There is a risk of resistance to change within established industries. Education and training are essential for overcoming these hurdles. As the demand for sustainable products grows, so does the need for continuous improvement in manufacturing practices.
Market Trends Shaping the Future of Power Resistors in 2026
The market for power resistors is evolving rapidly. As technology advances, the demand for efficient energy management increases. Several trends are shaping this landscape, including the push for miniaturization. Manufacturers are developing smaller, yet powerful resistors. This trend is essential for applications in compact electronics and electric vehicles.
Another key trend is the focus on sustainability. Companies are seeking eco-friendly materials for resistor production. This shift impacts the entire manufacturing process. It encourages innovation in material science and promotes recycling efforts. Yet, there are challenges to address, such as finding sustainable alternatives that meet performance standards.
The integration of smart technologies is also noteworthy. Smart sensors are becoming part of power resistor systems. They enhance reliability and performance monitoring. This trend raises questions about the cost and complexity of implementation. Will it lead to smarter but more expensive systems? As we move towards 2026, these dynamics will likely push the boundaries of what's possible in power resistor technology.
2026 Power Resistors Market Trends
Related Posts
-

Unveiling the Future: How Solid State Technology is Revolutionizing Modern Electronics
-
Navigating Trends in Electronic Components at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

2025 Top 10 Electronics Marketplace Trends: What to Expect in Online Shopping
-
Exploring the Future: How Capacitors Can Transform Sensing Technology
-
Unlocking Innovation: How Electronic Components Drive the Future of Technology
-
Exploring the Future of Electronic Components: Innovations and Insights from Leading Suppliers
