News / Blog
Top 10 Best Capacitors Inductors and Resistors for Your Electronics Projects?
In the realm of electronics, understanding the role of capacitors, inductors, and resistors is crucial. John Smith, a leading expert in electronic components, once said, “Choosing the right capacitors, inductors, and resistors can make or break your project.” This statement highlights the importance of selecting quality components for reliable performance.
Capacitors store energy, inductors manage current flow, and resistors control voltage. These components are fundamental in creating circuits that function correctly. For hobbyists or professionals, knowing what works best enhances outcomes. However, even experienced engineers sometimes overlook the nuances in these materials. For instance, a capacitor's lifespan can vary significantly based on usage and type.
Projects often face challenges, impacting the choice of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. Budget constraints may lead to compromises in quality. This can be a mistake. Selecting subpar components may result in circuit failures. It’s essential to reflect on past projects and learn from these choices. Ultimately, the right components pave the way for innovation in electronics.
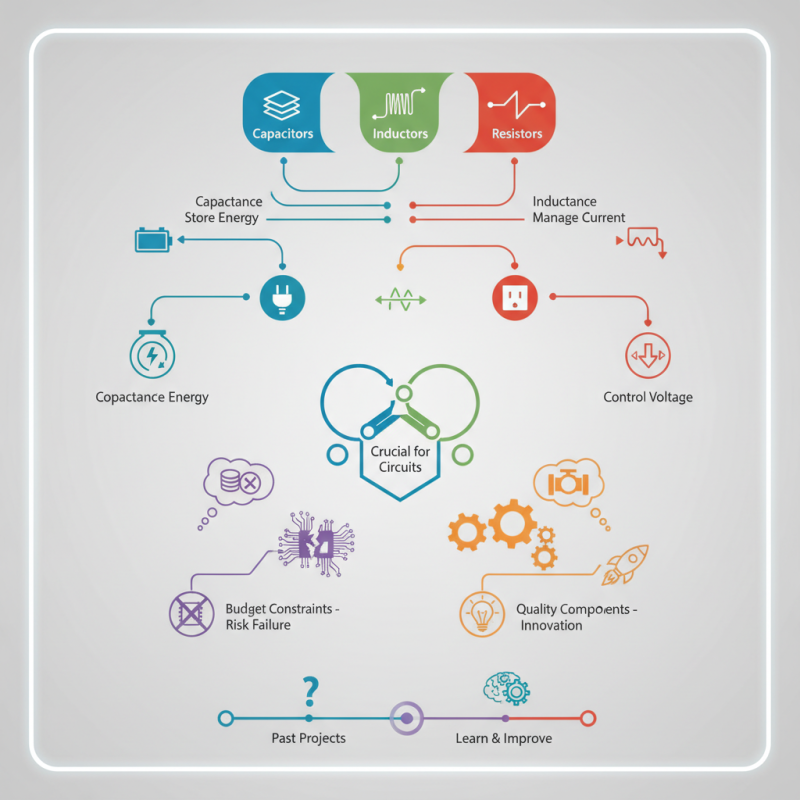
Understanding the Role of Capacitors, Inductors, and Resistors
Capacitors, inductors, and resistors are fundamental components in electronics. They each play a unique role. Capacitors store energy, allowing for smooth voltage fluctuations. Inductors store energy in a magnetic field, controlling current flow. Resistors limit current, protecting circuits and managing power distribution.
When choosing capacitors, consider their voltage rating and capacitance value. It's important they match your project’s requirements. For inductors, pay attention to their inductance and current rating. A mismatch can lead to inefficient performance. Resistors come in various types, like fixed and variable. Understand the specific resistance needed for your project.
Tips: Always check the specifications before purchasing. Ordering the wrong component can delay your project. Consider testing components in a breadboard setup before finalizing your design. Sometimes, a small adjustment in resistance can lead to big changes in performance. Reflecting on past mistakes can enhance your understanding and lead to better choices.
Criteria for Selecting the Best Components for Electronics Projects
Selecting the best components for your electronics projects can be challenging. The right capacitors, inductors, and resistors will greatly affect performance. One important criterion is your project's specific requirements. Determine the voltage and current ratings needed. Each component has unique characteristics that can influence your design.
Another key factor is component tolerance. Variability can impact circuit behavior. For example, a resistor with a high tolerance may not provide the accuracy needed for precision applications. It's wise to analyze how variations may affect your overall project. Explore and test different options to find the best fit, as refining your selection can lead to better outcomes.
Lastly, consider size and form factor. Space can be critically limited in some designs. A compact capacitor might seem appealing, yet it could have limitations in capacitance. Additionally, research the temperature and environmental factors your project may face. Don’t overlook how external conditions can affect component performance. Making choices that adapt to your needs requires careful thought and adjustment.
Top 10 Best Capacitors Inductors and Resistors for Your Electronics Projects
| Component Type | Value / Specifications | Voltage Rating | Package Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitor | 10 µF | 25V | Radial | Decoupling |
| Inductor | 10 mH | 30V | SMD | Power Supply Filtering |
| Resistor | 220 Ω | 0.25W | Axial | Current Limiting |
| Capacitor | 100 nF | 50V | Ceramic | Filtering |
| Inductor | 1 mH | 100V | Through Hole | Noise Filtering |
| Resistor | 1 kΩ | 0.5W | SMD | Biasing |
| Capacitor | 47 µF | 16V | Aluminum Electrolytic | Power Supply Smoothing |
| Inductor | 5 mH | 12V | Shielded | RF Applications |
| Resistor | 4.7 kΩ | 1/4W | Surface Mount | Pull-up Resistor |
| Capacitor | 1 µF | 16V | Film | Signal Coupling |
Top Capacitors: Types, Specifications, and Applications

When choosing capacitors for your electronics projects, consider the type you need. Capacitors come in various forms, such as ceramic, electrolytic, and film. Each type serves different purposes. For example, ceramic capacitors are often used for high-frequency applications. They are stable and compact. Electrolytic capacitors, on the other hand, are ideal for filtering and energy storage due to their high capacitance values.
Specifications are crucial. Look at voltage ratings and capacitance values. A capacitor's voltage rating dictates its reliability in a circuit. If you exceed this rating, it can fail. Measuring capacitance helps in selecting the right one. Some capacitors might not perform well in extreme conditions. Plan for temperature variations and other environmental factors.
Applications vary widely. In audio equipment, you might prefer film capacitors for clarity. For power supply circuits, electrolytic capacitors usually work best. Reflecting on your project's needs will guide your selection. Sometimes, picking the right capacitor isn’t straightforward. Experimentation can lead to better performance, but sometimes it may just complicate things further. Be prepared to iterate based on results.
Top Inductors: Types, Specifications, and Applications
Inductors are crucial for various electronics projects. They store energy in magnetic fields. Often used in filters, they help in tuning circuits smoothly. Some types include air-core, iron-core, and toroidal inductors. Each type has unique benefits catering to specific applications.
For instance, air-core inductors are prized for their low loss but may lack compactness. On the other hand, iron-core inductors provide higher inductance per volume. According to recent industry data, the market demand for inductors is projected to grow by over 4% annually. This growth is driven by the rise of consumer electronics and renewable energy technologies.
Understanding specifications is vital. Inductance value, measured in henries, informs the performance level. A higher inductance means more stored energy, but it can lead to size issues. Additionally, self-resonant frequency must be accounted for. Improper choices can lead to degraded performance. Whether in a DIY project or an advanced prototype, choosing the right inductor is critical.
Top 10 Best Capacitors, Inductors, and Resistors for Your Electronics Projects
Top Resistors: Types, Specifications, and Applications
When working on electronics projects, selecting the right resistors is crucial. Resistors come in various types, each with specific specifications and applications. Understanding these differences can enhance your project’s performance. Common types include carbon film, metal film, and wire-wound resistors. Each has its unique characteristics, such as stability, noise, and temperature coefficient.
For those diving into new projects, here are some useful tips. Choose a resistor based on your circuit’s requirements. Power rating is essential. A resistor rated too low can overheat and fail. Don’t overlook tolerance. A resistor with high tolerance ensures more accurate results.
Knowing the purpose of each resistor type is key. Carbon film resistors are affordable and commonly used but might not be the best for precision applications. Metal film resistors offer lower noise and better accuracy. If your project involves high power, consider wire-wound resistors. They can handle more load but may not suit high-frequency applications. Keep experimenting, and don't hesitate to reflect on your choices. Every mistake is a learning opportunity.
Related Posts
-
Navigating Trends in Electronic Components at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-
Unlocking Innovation: How Electronic Components Drive the Future of Technology
-

2025 Top 10 Electronics Marketplace Trends: What to Expect in Online Shopping
-
Top Passive Components You Need to Know for Your Electronics Projects
-

Why Are Passive Components Essential in Electronic Circuits?
-

2026 Top Trends in Electronic Capacitors for Future Innovations?
