News / Blog
How to Choose Between Capacitors and Resistors for Your Electronic Projects
In the realm of electronics, the selection of passive components, particularly capacitors and resistors, is crucial for the performance and efficiency of any project. According to industry reports, the global market for electronic components is anticipated to grow significantly, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for electronics in various applications. Statistics reveal that the capacitor market is expected to reach over $45 billion by 2025, while the resistor market is on a growth trajectory, with a projected CAGR of 3.8% from 2020 to 2025. This rising demand underscores the importance of understanding how to effectively choose between capacitors and resistors to enhance circuit design and functionality.
Capacitors and resistors serve distinct purposes within electronic circuits. Capacitors store and release energy, playing a vital role in applications such as filtering, timing, and energy coupling, while resistors are fundamental to controlling current flow and establishing voltage levels. A well-informed selection process that weighs the specifications and functionalities of capacitors and resistors is essential for creating reliable and efficient electronic projects. This guide aims to provide insights into how to make an informed choice between these two critical components, fostering better design practices and ultimately contributing to the success of your electronic endeavors.

Understanding the Roles of Capacitors and Resistors in Circuits
Capacitors and resistors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, each serving distinct roles that are crucial for the proper functioning of devices. Resistors are primarily used to limit the flow of electric current and to divide voltages. By doing so, they help protect sensitive components from excessive current, thereby ensuring stability and reliability in the circuit. The resistance value is measured in ohms, and choosing the right resistor is essential for maintaining the desired current and voltage levels.
On the other hand, capacitors store and release electrical energy, acting as temporary energy sources in a circuit. They are essential for filtering, smoothing out voltage fluctuations, and decoupling components from one another. Capacitors are characterized by their capacitance, measured in farads. In applications like timing circuits or signal processing, capacitors work alongside resistors to influence the time constants of circuits, creating delays or shaping signal waveforms. Understanding these roles helps in making informed decisions about which component to implement for the desired functionality in electronic projects.
Key Differences Between Capacitors and Resistors
Capacitors and resistors are fundamental components in electronic projects, each serving distinct yet vital roles. The primary difference between the two lies in their function within an electrical circuit. Capacitors are designed to store and release electrical energy, enabling them to smooth out voltage fluctuations and filter signals. Recent industry reports indicate that the global capacitor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2021 to 2026, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient electronics and renewable energy systems. This showcases the critical nature of capacitors in various applications, particularly in power supply and signal processing.
On the other hand, resistors are used to regulate the flow of electric current, providing precise control over voltage and current distribution within a circuit. The resistor market is also expanding, with estimates suggesting a growth rate of approximately 3.7% annually, largely due to their essential role in the design of integrated circuits and consumer electronics. Resistors dissipate energy in the form of heat, which is a critical factor in circuit design to prevent damage to sensitive components. Understanding the unique properties and applications of resistors and capacitors is crucial for engineers and hobbyists alike, as the choice between them can significantly affect the functionality and efficiency of electronic devices.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Components for Projects
When selecting components for electronic projects, understanding the primary functions of capacitors and resistors is essential. First, consider the role each component plays within the circuit. Capacitors store and release electrical energy, making them ideal for applications where quick discharging and charging are necessary, such as in filtering and timing circuits. On the other hand, resistors primarily limit current flow and divide voltage, which is crucial for protecting sensitive components and establishing desired operating conditions within a circuit.
Another important factor to consider is the operating environment and electrical characteristics required for your project. For instance, if you’re working in a high-frequency application, capacitor selection is influenced by factors like Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and self-resonant frequency. In contrast, when dealing with resistors, consider their power rating and tolerance to ensure they can handle the load without overheating or affecting circuit performance. By assessing these parameters and understanding how they relate to your project's specific requirements, you can effectively choose between capacitors and resistors to optimize your electronic designs.
How to Choose Between Capacitors and Resistors for Your Electronic Projects - Factors to Consider When Choosing Components for Projects
| Component Type | Key Use Cases | Advantages | Disadvantages | Factors to Consider |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitor | Energy storage, smoothing out voltage fluctuations | Fast response time, lightweight | Limited lifespan, can leak charge | Capacitance value, voltage rating, size constraints |
| Resistor | Current limiting, voltage division | Stable performance, easy to use | Generates heat, can affect signal quality | Resistance value, power rating, tolerance level |
| Capacitor | Filtering and coupling in audio applications | Improves sound quality, reduces noise | Frequency response limitations | ESR value, frequency characteristics |
| Resistor | Biasing transistors in circuits | Essential for controlling current flow | Can limit circuit speed | Operating environment, ambient temperature |
Applications and Use Cases for Capacitors vs Resistors
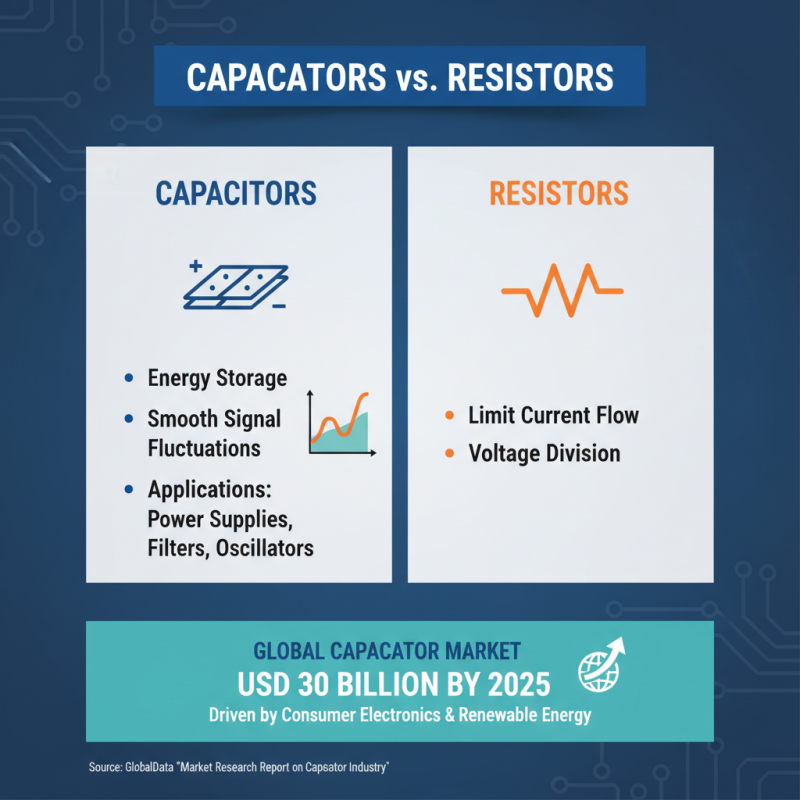
When considering electronic projects, understanding when to use capacitors versus resistors is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Capacitors are often utilized in applications requiring energy storage and smooth signal fluctuations, making them ideal for power supply systems, filtering circuits, and oscillators. According to the "Market Research Report on Capacitor Industry" published by GlobalData, the global capacitor market is expected to reach USD 30 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand in sectors like consumer electronics and renewable energy, where their ability to maintain voltage levels and enhance energy efficiency is vital.
On the other hand, resistors play a fundamental role in controlling current flow within circuits, making them essential for voltage division, current limiting, and biasing applications. A study by ResearchAndMarkets indicates that the resistor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% over the next five years, largely due to their widespread use in automotive electronics and industrial machinery. The ability of resistors to provide stable performance under a variety of temperatures and conditions makes them indispensable in circuit design, particularly in applications like signal attenuation and thermal management. Understanding their specific functions and applications can significantly enhance the effectiveness of an electronic project.
Best Practices for Selecting the Right Component for Your Needs
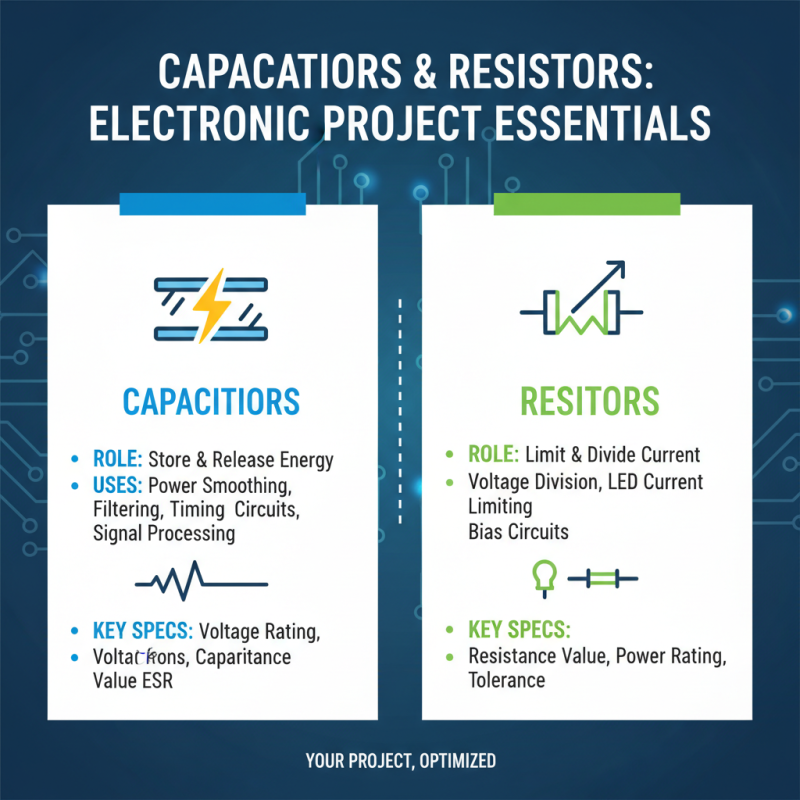
When selecting components for your electronic projects, understanding the roles and characteristics of capacitors and resistors is crucial. Capacitors store and release energy, making them ideal for smoothing out fluctuations in power supply or filtering applications. If your project involves timing circuits or signal processing, capacitors should be your go-to choice. They are essential in applications where temporary energy storage or phase shifting is required. When assessing capacitors, consider the voltage rating, capacitance value, and equivalent series resistance (ESR) to ensure optimal performance.
On the other hand, resistors are fundamental for controlling current flow and dividing voltage in a circuit. They can be used to limit current to protect sensitive components, create voltage dividers, or establish specific biasing conditions. When choosing resistors, pay attention to the resistance value, power rating, and tolerance level. For high-precision applications, consider low-temperature coefficient resistors to maintain performance across various conditions. Both components have unique functionalities, so understanding your project's specific needs—whether it requires energy storage and filtering or current regulation—will guide your decision in selecting between capacitors and resistors effectively.
Related Posts
-
Unlocking the Future: How Cutting-Edge Electronics News is Transforming Our Daily Lives
-
2025 Guide: How to Make Wise Electronic Components Purchases for Your Projects
-

2025 Top 5 Essential Electronic Parts You Can't Afford to Miss
-
Top 10 Electronics Products You Need to Upgrade Your Life Today
-

2025 Top 10 Electronic Websites to Transform Your Online Shopping Experience
-

Unveiling the Future: How Solid State Technology is Revolutionizing Modern Electronics
