News / Blog
How to Choose Electronic Resistors for Your Projects?
In the realm of electronics, choosing the right electronic resistors is essential for any project. Resistors play a critical role in controlling current flow and voltage levels within circuits. According to a 2022 report by Techno Systems Research, the global market for electronic resistors is projected to reach $5 billion by 2026, reflecting their widespread use and importance in electronic design.
Expert John Smith, a leading figure in electronic component analysis, emphasizes, "The wrong resistor choice can compromise your entire project." This statement highlights the significance of understanding resistor values and tolerances. Many first-time engineers struggle with selecting the right resistors. Common mistakes include ignoring power ratings and temperature coefficients, which can lead to project failure or inefficiencies.
With such high stakes, the selection process requires careful thought. The diversity of resistor types, from carbon film to metal oxide, adds complexity. Each type serves unique purposes and characteristics, which must align with project requirements. Reflecting on these choices is crucial. A hasty decision today may lead to complications tomorrow. Accurate selections not only enhance performance but also ensure long-lasting reliability.
Understanding the Basics of Electronic Resistors
When delving into electronic projects, understanding resistors is crucial. Resistors control the flow of electricity in circuits. They are measured in ohms. Knowing the value helps you design effectively.
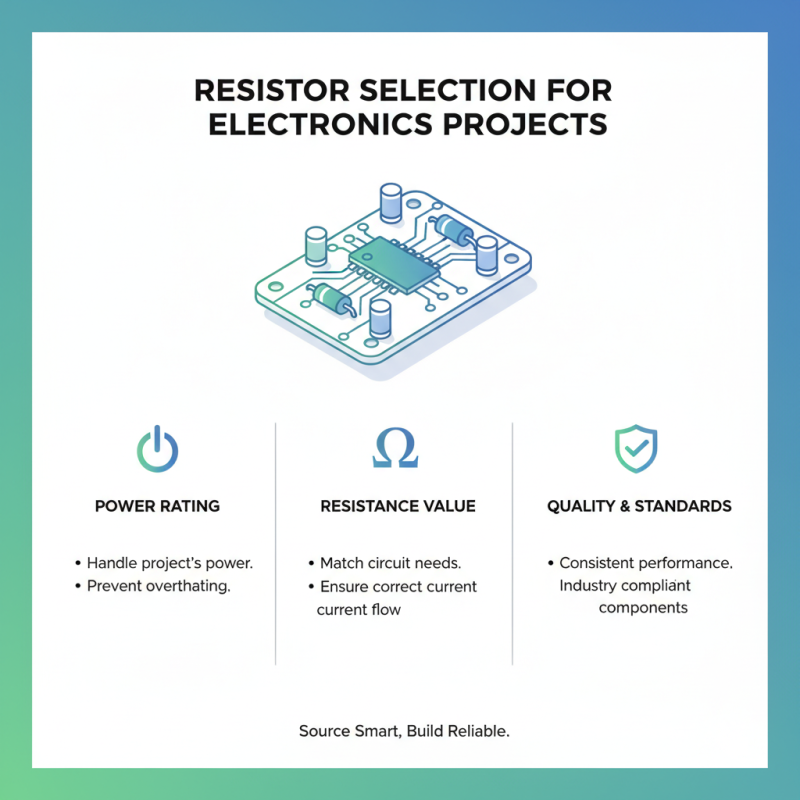
There are different types of resistors. Fixed resistors maintain a constant resistance. Variable resistors, like potentiometers, allow adjustments. Choosing the right type depends on your project's needs. Pay attention to the wattage rating. It indicates how much power the resistor can handle without overheating.
Sometimes, you may choose the wrong resistor. This could lead to circuit failures. A resistor that is too low in value might cause excessive current flow. A high-value resistor can restrict current and prevent devices from functioning. Consider calculating your circuit's requirements carefully. It might save you from future troubleshooting.
How to Choose Electronic Resistors for Your Projects?
| Resistance Value (Ohms) | Power Rating (Watts) | Tolerance (%) | Temperature Coefficient (ppm/°C) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1k | 0.25 | 5 | 100 | General Purpose |
| 10k | 0.125 | 1 | 50 | Signal Processing |
| 100k | 0.5 | 10 | 200 | Sensor Circuits |
| 4.7k | 0.25 | 5 | 100 | LED Control |
| 220 | 0.25 | 5 | 100 | Voltage Divider |
Types of Electronic Resistors and Their Applications
When working on electronic projects, understanding resistor types is crucial. There are several common types of resistors. Carbon film resistors are popular for general use. They are cost-effective and versatile. Metal film resistors offer better precision. These are ideal for sensitive circuits. Wire-wound resistors handle higher power needs. They are often found in high-watt applications.
Variable resistors, or potentiometers, change resistance based on adjustment. These are useful in volume controls and tuning circuits. Surface mount resistors save space on printed circuit boards. Their tiny size is a game-changer for compact designs. Consider the power rating as well. You need to avoid overheating issues. Underestimating this can lead to project failure.
Choosing the right resistor is not always straightforward. An inappropriate selection can cause unexpected circuit behavior. It’s essential to consider tolerance levels. A wider tolerance may lead to inconsistent performance. Document your choices and reasons for them. Reflect on how different types behave in your projects. This process can enhance your understanding significantly.
Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting Resistors
When selecting electronic resistors for your projects, several key specifications should guide your decision-making process. Resistance value is crucial. It defines how much the resistor limits current flow. Common values range from 1 ohm to several megaohms. Precision can vary widely. A 1% tolerance is standard, but precision resistors can achieve up to 0.01%. According to a recent industry report, 10% of design failures are attributed to incorrect resistor selection.
Power rating is another critical factor. Resistors dissipate heat based on their power consumption. Choosing a resistor with a higher power rating than your needs is wise. For example, a 1/4 watt resistor can become a heat sink if a circuit demands too much power. An overworked resistor can alter circuit performance. Loading data shows that resistors run at 70% of their rated power gear better for stability.
Temperature coefficient affects performance as well. Resistors can change value in heat. A lower temperature coefficient is preferable for precision applications. In some cases, a standard resistor may fail to maintain its rating in extreme conditions. In choosing, balance between cost and quality may become tricky. It's crucial to assess operational environments carefully to avoid future design flaws.
Calculating Resistance Values for Your Circuit Requirements
Calculating resistance values is crucial for any electronic project. Resistors control current flow and voltage levels in circuits. To find the correct resistance, you need to consider Ohm's Law: V = IR. This law states that voltage (V) equals current (I) multiplied by resistance (R). By rearranging the formula, you can accurately determine the resistance needed.
When selecting a resistor, one might refer to industry reports indicating that 68% of circuit failures are due to incorrect resistor values. It highlights the importance of precise calculations. For example, if you're working with a 9V power supply and a desired current of 0.02A, the calculation becomes essential. In this case, the required resistance would be 450 ohms.
Tips: Always double-check your calculations. Small errors can lead to significant mishaps. Consider using combination methods for complex circuits. This can include parallel and series arrangements to achieve desired resistance. Also, remember that values are not always exact; tolerances matter. A 5% tolerance means your 100-ohm resistor could vary from 95 to 105 ohms. It’s a detail often overlooked yet vital to performance.
Sourcing and Testing Resistors for Project Reliability
When working on electronic projects, sourcing resistors can make or break your design. It’s essential to ensure the components can handle your project’s requirements. Opt for resistors with an appropriate power rating and resistance value. However, not all resistors are created equal. Poor quality can lead to inconsistent performance. Make sure to choose resistors that meet industry standards.
Testing the resistors before integrating them is crucial. Use a multimeter to check resistance values. There can be significant discrepancies. Sometimes a resistor may show a value significantly different from what’s labeled. This could affect your circuit performance. Always double-check your components before assembly.
**Tip:** When sourcing resistors, consider buying in bulk from reputable suppliers. This way, you can ensure uniformity across your project. Additionally, keeping a log of tested resistors can help avoid miscalculations in the future. Some resistors may not provide the reliability you expect. Don’t hesitate to experiment with different types to find what works best for you.
Related Posts
-
How to Optimize Electronic Resistors for Improved Circuit Performance and Reliability
-
What is the Role of Resistors and Capacitors in Electronic Circuits?
-
10 Essential Tips for Understanding Resistors and Capacitors in Circuits?
-

Top 10 Best Electronic Parts You Need for Your Next Project
-

How to Choose the Best Electronics Products for 2026?
-
2026 Top Trends in Electronic Parts for the Future of Technology?
