News / Blog
How to Choose the Right Resistors and Capacitors for Your Electronics Projects
Selecting the appropriate resistors and capacitors is a critical step in the design and development of electronic projects. According to a recent report by the Market Research Future, the global passive component market, which includes resistors and capacitors, is expected to reach approximately $50 billion by 2027, driven by the increasing demand for electronics in various applications such as consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial automation. This surge in demand underscores the importance of understanding how to choose the right components to ensure optimal performance and reliability in electronic circuits.
Resistors and capacitors serve essential functions in electronic designs, including voltage division, signal filtering, and stability enhancement. Choosing the wrong values or types can lead to circuit failures, inefficiencies, or even damage to sensitive components. Industry experts emphasize that factors such as tolerance, temperature coefficient, and equivalent series resistance (ESR) play significant roles in component selection. For instance, a study published in the IEEE Transactions on Electronics highlighted that improper capacitor selection can result in signal distortion and reduced power efficiency, particularly in high-frequency applications. As more engineers and hobbyists engage in electronics design, understanding how to effectively select resistors and capacitors becomes paramount to achieving successful outcomes.
Understanding Resistors: Types and Their Functions
Understanding resistors is crucial for any electronics project. Resistors are passive components that limit the flow of electrical current in a circuit, ensuring that other components receive the correct voltage and current levels. There are various types of resistors, including fixed, variable, and digital types, each serving unique functions. Fixed resistors maintain a constant resistance, while variable resistors, like potentiometers, allow for adjustable resistance. Use these components to achieve specific voltage drops across devices or to set tailored signal levels.
When selecting resistors, consider their power rating, which indicates how much power they can dissipate without overheating. Additionally, the tolerance of a resistor shows how much its resistance value can deviate from the stated value, impacting precision in your project.
Tips: Always match the resistor's power rating to your project requirements to avoid failures. When choosing resistors for high-frequency applications, prefer metal film resistors for improved performance. Consider using a multimeter to measure and confirm the resistance values of your components before soldering them into your circuit to ensure reliability.
Exploring Capacitors: Varieties and Applications
Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, serving various functions depending on their type and application. There are several varieties of capacitors, including ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, and film capacitors, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific tasks. For example, ceramic capacitors are widely used in high-frequency applications due to their minimal inductance, while electrolytic capacitors are preferred for power supply filtering because of their high capacitance values.
In addition to their basic types, capacitors can be categorized based on their voltage ratings, temperature coefficients, and tolerances. Understanding these characteristics is critical for selection in any electronics project. For instance, tantalum capacitors have a higher energy density than their electrolytic counterparts, making them ideal for applications in compact devices like smartphones. However, they are more sensitive to overvoltage situations, necessitating careful consideration when integrating them into a circuit. Ultimately, the choice of capacitor directly impacts circuit performance, influencing factors such as stability, efficiency, and overall functionality.
Determining the Right Specifications for Your Project
When embarking on electronics projects, selecting the right resistors and capacitors is crucial for ensuring circuit functionality and reliability. To determine the appropriate specifications for these components, one must first consider the electrical requirements of the project. For resistors, key specifications include resistance value (measured in ohms), power rating (often in watts), and tolerance. According to the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA), a common tolerance range for resistors is ±5% for carbon film types, while precision resistors can be found with tolerances as tight as ±0.1%. Choosing a resistor with the correct power rating is equally vital; exceeding this rating can lead to overheating and component failure.
For capacitors, specifications such as capacitance value (in farads), voltage rating, and operating temperature range are essential. Capacitors are often categorized based on their dielectric materials, with ceramic capacitors generally offering lower capacitance values and electrolytic capacitors providing higher values but with polarity considerations. Data from the IEEE indicates that capacitors with voltage ratings significantly above the circuit's operating voltage can enhance reliability, reducing the risk of breakdown. Moreover, understanding the frequency response of capacitors is important for applications involving AC signals. For example, high-frequency applications may require capacitors with low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) to minimize energy losses, a specification often highlighted in component datasheets. Each detail plays a vital role in achieving optimal performance in electronics projects.
Calculating Resistance and Capacitance Values Accurately
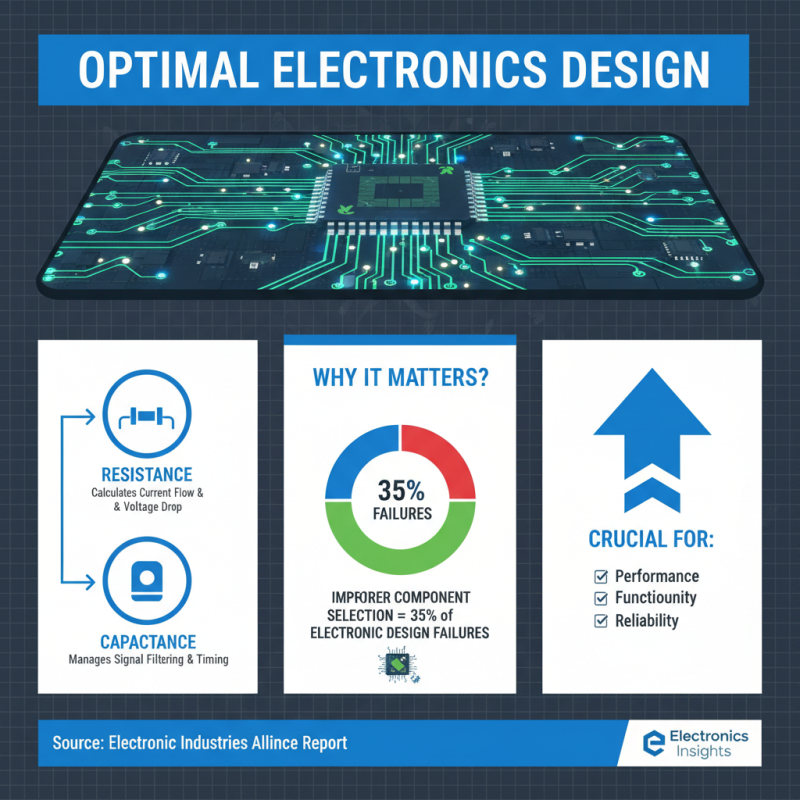
When embarking on electronics projects, calculating resistance and capacitance values accurately is crucial to achieving desired performance and functionality. Resistors and capacitors are fundamental components that can significantly influence the behavior of circuits. According to a report by the Electronic Industries Alliance, about 35% of electronic design failures are attributed to improper component selection, highlighting the importance of meticulous calculations.
To calculate resistance, Ohm's Law (V = IR) serves as a fundamental principle. Designers must understand the voltage across the component and the current flowing through it to determine the appropriate resistor value. Additionally, the tolerance levels of resistors are essential; components with tighter tolerances (such as 1% or 0.5%) provide more predictable behavior in sensitive applications. Similarly, for capacitors, capacitance values are often defined in farads, with microfarads (µF) being common for many circuits. The charging and discharging behavior of capacitors is described by the time constant formula τ = RC, where R is resistance and C is capacitance. Selecting the correct values ensures optimal performance, especially in timing circuits or filtering applications.
Industry studies emphasize the significance of factoring in environmental conditions, as temperature variations can affect resistance and capacitance values. The IPC-2221 standards assert that component performance can drift significantly outside typical operating temperature ranges, which can cause deviations in the expected outcomes of electronic designs. Thus, engineers must carefully calculate and choose components that align not only with theoretical specifications but also with real-world performance expectations to enhance reliability and functionality in their projects.
Tips for Sourcing Quality Electronic Components
When sourcing quality electronic components like resistors and capacitors for your projects, it's crucial to consider several factors to ensure you're making the right choice. One of the primary considerations is the specifications of the components themselves. Understand the voltage ratings, tolerance levels, and temperature coefficients relevant to your application. This foundational knowledge will help you select components that perform optimally and enhance the reliability of your electronics projects.
Another essential aspect is the sourcing process. It's advisable to purchase components from reputable suppliers who provide detailed specifications and datasheets. Look for suppliers that have a transparent quality assurance process, as this reduces the likelihood of receiving counterfeit or substandard parts. Additionally, checking customer reviews and seeking recommendations within electronic communities can guide you toward trustworthy sources. By focusing on these elements, you can ensure that the resistors and capacitors you select are of high quality and suitable for your specific electronic needs.
Related Posts
-

The Hidden Importance of Active Components in Everyday Products
-
How to Optimize Electronic Resistors for Improved Circuit Performance and Reliability
-

Why Electronic Capacitors Are Essential for Modern Electronics
-

Why Electronics Products are Essential for Modern Living and How to Choose the Best Ones
-

2025 Top 5 Essential Electronic Parts You Can't Afford to Miss
-
Why Staying Updated on Electronics News is Essential for Tech Enthusiasts Today
