News / Blog
Top Electronic Parts Everyone Should Know About?
In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, understanding key electronic parts is essential for anyone in the industry. With the global electronic components market expected to reach $1 trillion by 2025, familiarity with these components can drive innovation. According to Dr. Alice Tran, a leading expert in electronic parts, "Knowledge of basic components is crucial for all engineers." Her insights emphasize the importance of foundational knowledge in an increasingly complex environment.
Electronic parts serve as the backbone of modern technology, from smartphones to industrial machinery. Components such as resistors, capacitors, and microcontrollers play pivotal roles. However, even seasoned professionals may underestimate their significance. Neglecting to grasp these fundamentals can lead to costly errors in design or production.
The rapid pace of change also poses challenges. New materials and technologies emerge constantly, making it difficult to keep up. Yet, a strong grasp of electronic parts can help professionals adapt and innovate. By reflecting on our understanding of these components, we can better navigate the industry's demands and contribute meaningfully to advancements in technology.

Essential Components of Electronic Circuits and Their Functions
When diving into electronic circuits, understanding essential components is crucial. Resistors are fundamental. They limit the flow of current, protecting sensitive parts. You can easily spot them by their colored bands. Capacitors store electric energy for short bursts. They help smooth out fluctuations in circuits. Without them, devices could malfunction.
Another key component is the diode. It allows current to flow in one direction only. This property is vital for controlling circuit behavior. Transistors act as switches or amplifiers. They can regulate current flow significantly. You’ll find them in nearly every device we use today. Yet, the placement of these components can often lead to issues if not done carefully.
Breadboards are great for prototyping these circuits. However, mistakes in connections can lead to confusion. Each component has its unique function. Understanding their roles leads to better circuit design. This knowledge is essential but can take time to master. Embracing small errors along the way can lead to deeper learning and improvement.
Top Electronic Parts Everyone Should Know About
This chart represents the popularity of essential electronic components used in circuits. Resistors and capacitors are among the most widely recognized, while inductors and diodes also play critical roles in electronic functionality.
Understanding Resistors: Types, Specifications, and Uses
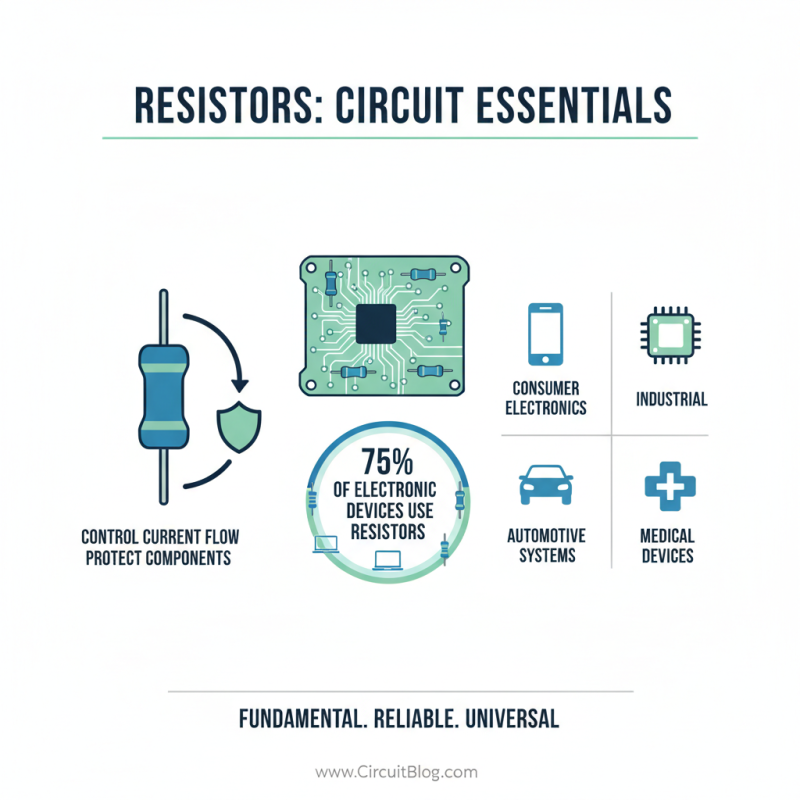
Resistors are fundamental components in electronic circuits. They control the flow of electric current and protect sensitive components. According to industry reports, nearly 75% of electronic devices use resistors. This shows their critical role in various applications, from consumer electronics to automotive systems.
There are several types of resistors. Fixed resistors are the most common. They have a constant resistance value. Variable resistors, like potentiometers, can change resistance. This adaptability is essential in tuning circuits. In contrast, specialty resistors like thermistors respond to temperature changes. They have unique specifications and are used in specific applications, like temperature sensors.
Understanding the specifications of resistors is vital. Resistance is measured in ohms. Tolerance indicates how much the resistance can vary. A typical tolerance is ±5%. However, in precision applications, tighter tolerances are needed. Construction materials also matter. Carbon film, metal film, or wire-wound resistors each have unique properties. These differences affect performance, heat dissipation, and reliability. Many engineers overlook these factors, leading to inefficient designs. Striking a balance between cost and functionality is essential.
Capacitors: Importance, Varieties, and Applications in Electronics
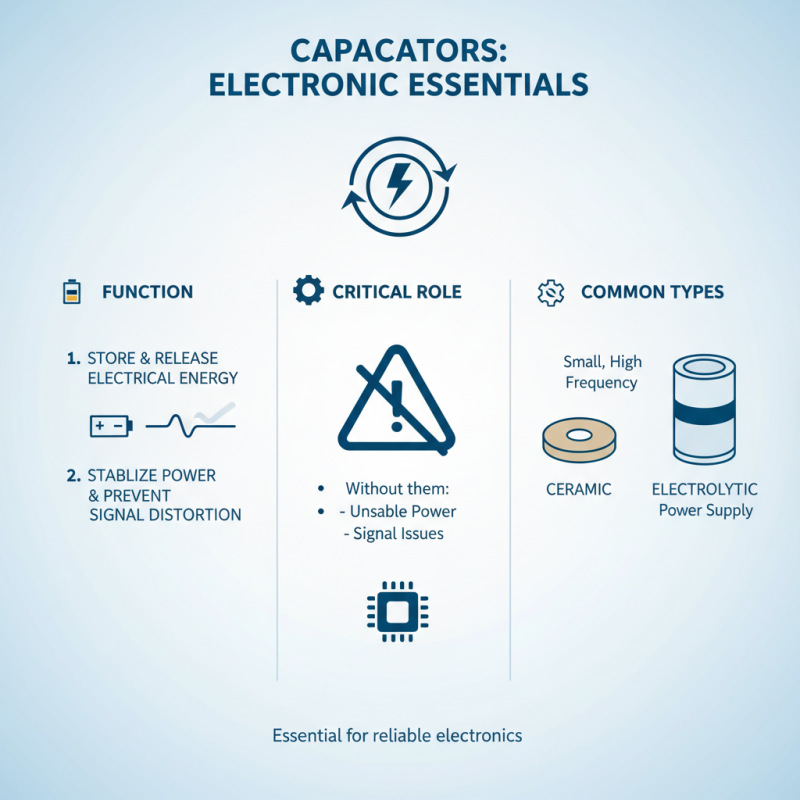
Capacitors play a critical role in electronics. They store and release electrical energy, making them essential in various applications. Without them, devices would face issues like unstable power supply and signal distortion. Capacitors come in different types, each suited for specific needs. Ceramic and electrolytic capacitors are among the most commonly used.
Ceramic capacitors are small and reliable. They are often found in RF applications due to their stability. On the other hand, electrolytic capacitors provide higher capacity but need proper handling. Their polarity makes them more prone to damage if connected incorrectly. This is an area where beginners often falter.
In addition to these, film capacitors are also noteworthy. They have excellent insulation properties and are great for audio applications. However, they can be bulkier and costlier. Users should weigh the pros and cons to make the right choice. Understanding your needs will help you avoid mistakes. Capacitors are vital components that can make or break a project.
Diodes and Their Role in Controlling Electric Flow
Diodes are essential electronic components. They control the direction of electric flow in circuits. By allowing current to pass in one direction only, diodes protect sensitive parts. This creates a stable environment for devices to function correctly.
Understanding diodes is crucial for anyone interested in electronics. Their functionality influences how circuits operate. A common application is in power supplies where diodes rectify alternating current into direct current. This conversion ensures devices receive the appropriate energy type.
However, not all diodes are the same. They vary in specifications and purposes. Some handle higher voltages, while others work in low-power situations. Choosing the right diode for a project is not always easy. It requires careful consideration of the circuit's needs and potential limitations.
Transistors: The Building Blocks of Modern Electronics and Their Types
Transistors are the heart of modern electronics. They act as switches and amplifiers. Without them, many devices would not function as they do today. A common type is the bipolar junction transistor (BJT). This device uses both electron and hole charge carriers. It’s simple but effective, playing a key role in various applications.
Then, we have field-effect transistors (FETs). These control the flow of current using an electric field. They are often found in integrated circuits. FETs are more efficient than BJTs, especially for high-frequency applications. However, they can be sensitive to static. This sensitivity requires careful handling during development.
Another type is the metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). This transistor is widely used in digital circuits. It has a high input impedance. However, it can also be quite complex and challenging to use. Mistakes during the designing process can lead to failures. Understanding these nuances is crucial for anyone working with electronics.
Top Electronic Parts Everyone Should Know About - Transistors: The Building Blocks of Modern Electronics and Their Types
| Type of Transistor | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) | A type of transistor that uses both electron and hole charge carriers. | Amplifiers, switches, and signal modulation. |
| Field Effect Transistor (FET) | Transistor that depends on an electric field to control the flow of current. | Voltage amplifiers, signal processing, and analog switches. |
| Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FET (MOSFET) | A type of FET known for its high efficiency and low output noise. | Power applications, high-speed switching, and microprocessors. |
| Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) | Combines the benefits of both BJT and MOSFET technologies. | Electric vehicles, industrial motor drives, and renewable energy systems. |
| Darlington Transistor | A pair of BJTs connected to provide high current gain. | Signal amplifiers, relay drivers, and sensor applications. |
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Best Electronic Parts You Need for Your Next Project
-

2025 Top 5 Essential Electronic Parts You Can't Afford to Miss
-
How to Optimize Electronic Resistors for Improved Circuit Performance and Reliability
-

The Hidden Importance of Active Components in Everyday Products
-

Why Electronics Products are Essential for Modern Living and How to Choose the Best Ones
-
2025 Guide: How to Make Wise Electronic Components Purchases for Your Projects
