News / Blog
10 Essential Tips for Choosing Passive Electronic Components
Choosing the right passive electronic components is crucial for any electronic design. These components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, play a key role in circuit performance. It is essential to understand how each component impacts your project.
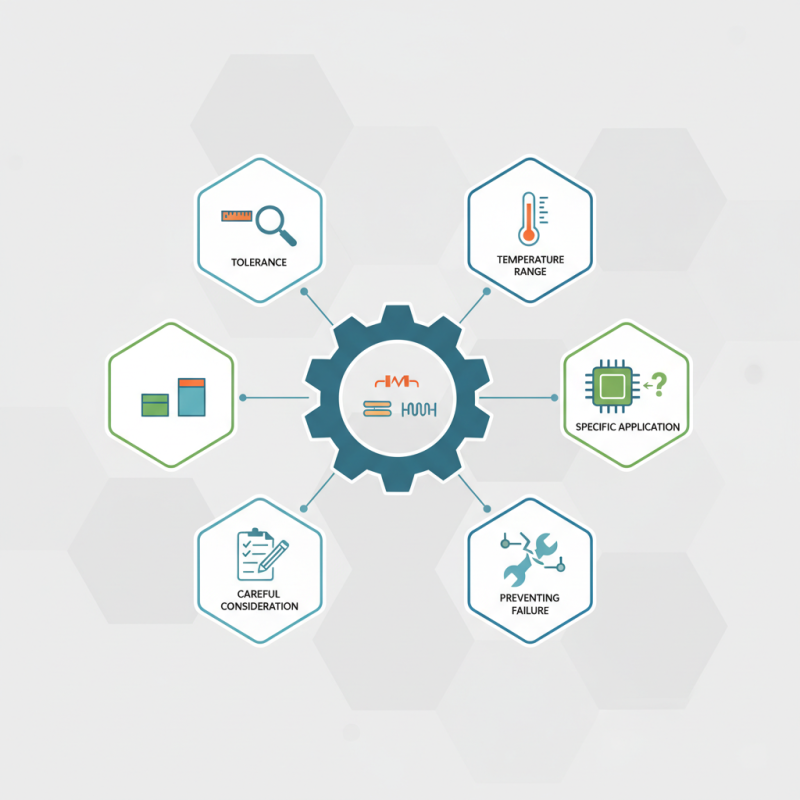
When selecting passive electronic components, consider factors like tolerance, temperature range, and size. Each choice can affect the overall functionality of your circuit. It is easy to overlook these details, but careful consideration can yield significant benefits. Moreover, an incompatible choice may lead to failure in your design.
You should also think about your specific application. Different projects have unique requirements that may not be immediately obvious. Misjudging a component's specifications can be costly in both time and resources. Therefore, batten down the hatches and be meticulous in your selection process. Passive electronic components might seem simple, yet they require careful analysis.
Understanding Passive Electronic Components: Key Types and Specifications
When selecting passive electronic components, understanding their key types and specifications is crucial. Passive components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. According to industry reports, capacitors account for over 30% of the global passive components market, projected to reach $124 billion by 2025. This shows their importance in modern electronics.
Resistors are fundamental in controlling current flow. They come in various types, such as carbon film and metal oxide. Choosing the wrong resistor can lead to circuit failures. For instance, a resistor’s tolerance can affect performance. Tolerances as high as 20% may seem acceptable at first glance, but they can introduce significant variability in sensitive applications.
Capacitors play critical roles in filtering and energy storage. They are categorized by dielectric materials, which impact their stability and performance. For example, ceramic capacitors are favored for their reliability but may not suit high-voltage applications. It’s essential to evaluate specifications thoroughly. An overlooked parameter can lead to design flaws and costly revisions. Understanding these nuances can make a difference in achieving optimal circuit functionality.
Analyzing the Impact of Tolerance and Rating on Component Selection
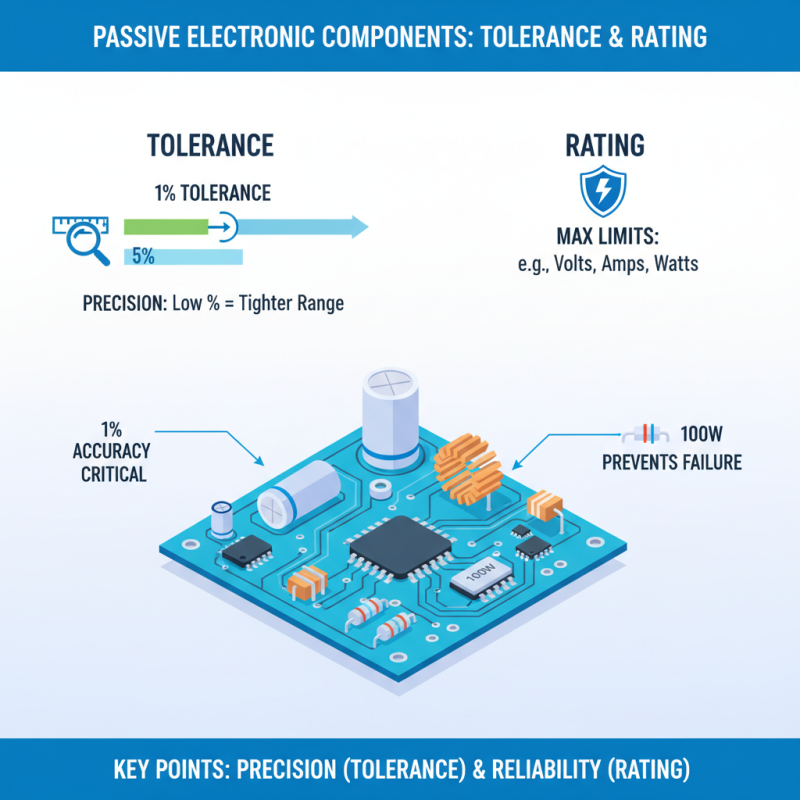
When selecting passive electronic components, tolerance and rating play crucial roles. Tolerance refers to the acceptable variation of a component's value. A high tolerance means more precise performance. For instance, a resistor with a tolerance of 1% will ensure a tighter range of resistance compared to one with 5%. This precision is vital for circuits requiring accuracy.
Rating describes the maximum load a component can safely handle. Exceeding this can lead to failure or damage. Consider a capacitor rated for 50 volts. Using it in a circuit with 70 volts could cause catastrophic results. Real-world applications often reveal how easy it is to overlook these details. Sometimes, engineers may underestimate these specifications, which can lead to ongoing design issues.
It's crucial to understand the specifications. Familiarity with these concepts helps in making better choices. Reflecting on past projects can uncover flaws in previous selections. This analysis is essential for future improvements. As technology advances, the importance of these factors remains undeniable.
Assessing Temperature Coefficients and Their Effect on Component Performance

When selecting passive electronic components, temperature coefficients play a crucial role in performance. These coefficients indicate how a component's resistance, capacitance, or inductance changes with temperature. A component with a high temperature coefficient may exhibit significant variations in performance under heat or cold. This can lead to unreliable circuit behavior and, ultimately, device failure.
Understanding the temperature range where a component operates is essential. Many components perform well at room temperature but fail outside that range. Take resistors, for example. Some have a temperature coefficient of ±50 ppm/°C, while others might be ±1000 ppm/°C. This difference can dramatically impact circuit stability. Choosing the right component requires thorough evaluation of these specifications.
It’s easy to overlook temperature effects in passive components. Engineers may focus solely on capacitance or resistance values. But neglecting temperature performance can lead to troublesome designs. Testing components under varying temperatures before full implementation may reveal issues. Ensuring components are suitable for the intended environment is key. A good design anticipates temperature fluctuations rather than just reacting to them.
Evaluating the Importance of Component Packaging and Footprint in Design
When designing electronic circuits, component packaging and footprint are often overlooked. Yet, these factors greatly influence performance and efficiency. According to a recent industry report, nearly 30% of design failures are attributed to poor component choices. This highlights the need to carefully evaluate packaging options.
The type and size of packaging affect both thermal management and electrical characteristics. For instance, surface mount devices (SMD) typically have a smaller footprint, making them suitable for compact designs. However, this can lead to overheating if not properly managed. Around 45% of engineers report encountering thermal issues in densely packed boards. Choosing the right packaging means balancing size with functionality.
Designers must also consider future scalability. A small footprint may seem appealing, but it could limit your design's upgrade path. Approximately 25% of engineers encounter challenges when trying to integrate new components into existing designs. Understanding the trade-offs between component size and overall system performance is crucial. The right choice is not always the obvious one. Reflecting on past designs can reveal these complexities.
10 Essential Tips for Choosing Passive Electronic Components
Comparing Cost vs. Performance Trade-offs in Passive Component Selection
When selecting passive electronic components, cost and performance are key factors. A recent industry report indicated that 40% of engineers cite high costs as a primary concern. However, these components play a crucial role in circuit behavior. An imbalance in performance can lead to poor product functionality.
Focusing on cost alone may compromise the quality of components. For instance, cheaper resistors may have higher tolerances, impacting accuracy. Consider using mid-range capacitors that provide better stability over time.
Tip: Always calculate total cost of ownership. Low upfront costs do not always mean lower lifetime expenses. Evaluate endurance and reliability. Balance this against your budget constraints. Building prototypes with various components can expose performance differences before mass production.
With continuous market changes, staying informed is vital. Some sources suggest that passive components are expected to grow in demand by 5% annually. Choosing wisely impacts both immediate projects and long-term strategies.
10 Essential Tips for Choosing Passive Electronic Components
| Component Type | Cost ($) | Performance Rating (1-10) | Lifetime (Hours) | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 0.10 | 8 | 50000 | -55 to 125 |
| Capacitor | 0.25 | 7 | 20000 | -40 to 85 |
| Inductor | 0.50 | 9 | 30000 | -55 to 125 |
| Ferrite Bead | 0.15 | 8 | 50000 | -40 to 125 |
Related Posts
-
Top Passive Electronic Components That Every Engineer Should Know?
-
Exploring the Growth of Passive Electronic Components at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Insights and Opportunities
-
2025 Guide: How to Make Wise Electronic Components Purchases for Your Projects
-

Top 5 Electronics Supply Sources for Your Next Big Project
-

2025 Top 5 Essential Electronic Parts You Can't Afford to Miss
-
Top Websites for Buying Electronic Components Online Easily and Affordably
