News / Blog
What Are Passive Components and How Do They Work in Electronics?
In the realm of electronics, passive components play a crucial role in circuit functionality and efficiency. As defined by Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in electronic engineering, "Passive components are the unsung heroes of circuitry, providing the essential support needed for active components to perform their tasks." These components, which include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not require a power source to operate, yet they are integral to the overall performance of electronic systems.
Understanding how passive components work is key for anyone involved in electronics, from hobbyists to seasoned engineers. These components help regulate voltage, store energy, and filter signals, enabling complex circuits to function harmoniously. Dr. Chen emphasizes the importance of mastering these components, stating that "A solid grasp of passive components is foundational to designing effective and reliable electronic devices." As technology continues to advance, the significance of these components remains ever-present, shaping the future of electronic design and innovation.

Definition of Passive Components in Electronics

Passive components are fundamental building blocks in electronics, defined as components that do not require an external power source to operate. Instead, they rely on the energy provided by the circuit in which they are inserted. Common examples include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. According to a recent industry report, passive components account for a significant share of the electronic components market, with a projected worth of approximately $51 billion by 2026. These components play critical roles in controlling current flow, storing energy, and filtering signals.
Resistors limit the flow of electrical current, capacitors store and release electrical energy, while inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. Each component operates based on passive properties, influencing how circuits behave under varying conditions. For instance, capacitors are integral to timing applications in oscillators, and they modify signal waveforms in power supply systems.
Tips: When designing circuits, consider the values and tolerances of passive components carefully, as they can significantly affect circuit performance. Moreover, staying updated with market trends and advancements in passive component technology can lead to more efficient designs and improved reliability, as indicated by industry forecasts predicting a rise in demand for high-performance passive components.
Types of Passive Components and Their Functions
Passive components are essential building blocks in electronic circuits, functioning without the need for external power sources. Their main types include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, each serving distinct purposes. Resistors limit the flow of electric current, effectively controlling voltage levels within a circuit and protecting sensitive components from damage. Capacitors store and release electrical energy, allowing for smooth voltage fluctuations and functioning as filters in power supplies and signal processing. Inductors, on the other hand, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through them, playing a crucial role in applications like transformers and electromagnetic interference suppression.
In addition to these primary components, passive devices also encompass various other forms such as diodes in certain configurations and connectors that facilitate signal transmission without amplification. Each of these components contributes to enhancing circuit functionality, stability, and efficiency. Understanding their specific roles allows engineers and designers to create reliable and effective electronic systems, catering to diverse applications from simple household devices to complex industrial machinery. The interplay between these passive components forms the groundwork of electronic circuit design, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of electronic equipment.
What Are Passive Components and How Do They Work in Electronics?
| Type of Passive Component | Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | Limits current and drops voltage | Voltage dividers, signal conditioning |
| Capacitor | Stores electrical energy | Filtering, decoupling, timing circuits |
| Inductor | Stores energy in a magnetic field | Power supply filters, radio frequency applications |
| Transformer | Changes voltage levels | Power distribution, audio applications |
| Diode (as passive) | Allows current to flow in one direction | Rectification, signal clipping |
The Role of Passive Components in Electronic Circuits
Passive components play a crucial role in the functioning of electronic circuits by managing and controlling the flow of electricity without the need for an external power source. These components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, each serving distinct functions that contribute to the overall performance of a circuit. Resistors limit current flow and divide voltages, which is essential in creating stable power conditions for active components. Capacitors, on the other hand, store and release electrical energy, making them vital in smoothing out voltage fluctuations and filtering signals. Inductors, with their ability to oppose changes in current, help in tuning and creating resonance within circuits.
In electronic circuit design, the importance of passive components cannot be overstated. They are often used in signal processing applications to filter unwanted noise, ensuring clean and accurate transmissions. Furthermore, passive components facilitate energy storage and delay signals, which is essential in timing circuits for various applications. By combining these components effectively, engineers can create circuits that are efficient and reliable, meeting the requirements of modern electronic devices without relying on active components' complex behaviors. This balance of passive and active elements is what makes advanced electronic systems function optimally.
Passive Components in Electronic Circuits
This chart illustrates the number of applications for various passive components used in electronic circuits. Resistors lead the way with the highest number of applications, followed by capacitors and inductors, demonstrating the vital role these components play in electronic design.
How Passive Components Affect Circuit Performance
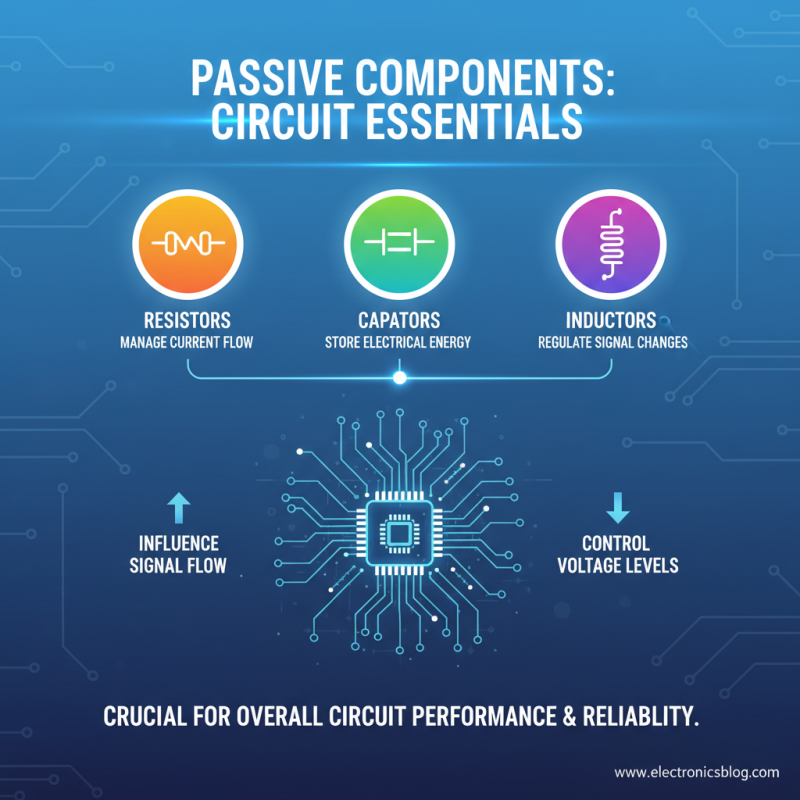
Passive components play a crucial role in the overall performance of electronic circuits. These components, which include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not require a power source to operate. Instead, they rely on the energy present in the circuit to perform their functions, influencing signal flow and energy storage. For example, resistors manage the current by providing resistance, which can affect the voltage levels in a circuit. This control over current and voltage is essential for ensuring that active components function correctly and reliably.
Furthermore, the interaction between passive components and circuit performance is significant when it comes to frequency response, impedance matching, and filtering. Capacitors, for instance, can smooth out voltage fluctuations and block direct current while allowing alternating current to pass through, thus enhancing signal integrity. Similarly, inductors can store energy in a magnetic field, affecting the circuit's response to changes in current. By carefully selecting and placing these passive components, engineers can optimize circuit efficiency, enhance stability, and improve the overall functionality of electronic devices. Understanding how these components interact helps ensure the design meets specific performance criteria, providing a reliable foundation for modern electronic applications.
Common Applications of Passive Components in Technology
In the world of electronics, passive components play a vital role in the functionality and efficiency of various technologies. These components, which include resistors, capacitors, inductors, and transformers, do not require an external power source to operate. Instead, they rely on the energy they harvest from the electrical signals they process. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global passive component market is expected to reach $60 billion by 2026, driven by increasing demand in sectors such as telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics.
Common applications of passive components are evident across various sectors. In telecommunications, for instance, capacitors are used for filtering and energy storage, ensuring clear signal transmission. Resistors facilitate voltage division and control current flow in electronic circuits, optimizing performance in power supplies and amplifiers. Additionally, passive components are essential in automotive applications, such as electric vehicle systems, where they help manage and distribute electrical energy efficiently. In recent years, advancements in passive component technology have led to smaller, more efficient designs, further enhancing their role in modern electronics.
Tips: When selecting passive components for your projects, always consider their specifications carefully. Look for components with a low tolerance for increased reliability and performance. Additionally, assess the thermal stability of components, as overheating can lead to failure in high-demand applications.
Related Posts
-
Top Passive Components You Need to Know for Your Electronics Projects
-
How to Select the Right Passive Components for Your Electronic Projects
-
Unlocking Innovation: How Electronic Components Drive the Future of Technology
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Electronic Components in Smart Technology Development
-
Exploring the Growth of Passive Electronic Components at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Insights and Opportunities
-
Exploring Market Trends for Electronic Components at the 2025 Canton Fair in China
