News / Blog
What is the Role of Resistors and Capacitors in Electronic Circuits?
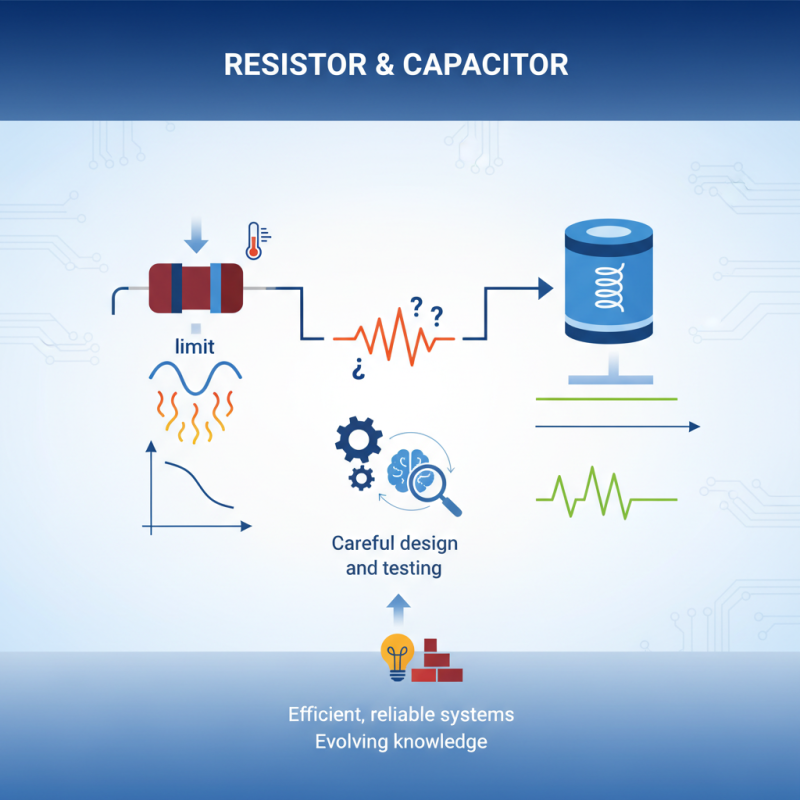
In the world of electronics, the function of resistors and capacitors is critical. These components play distinct roles yet work together to control current and voltage. Resistors limit the flow of electric current, ensuring circuits operate within safe parameters. They convert electrical energy into heat, which can sometimes lead to inefficiencies.
On the other hand, capacitors store and release energy. They can smooth out fluctuations in voltage, providing stability to the circuit. However, the interaction between resistors and capacitors is not always perfect. Sometimes, their behavior can be unpredictable, leading to unexpected results. This highlights the importance of careful design and testing in electronic projects.
Understanding the roles of resistors and capacitors can enhance circuit design. It helps engineers create more efficient, reliable systems. Yet, even seasoned professionals must continuously learn. Each circuit presents unique challenges, reminding us that knowledge is always evolving.
Understanding Resistors: Definition and Function in Circuits
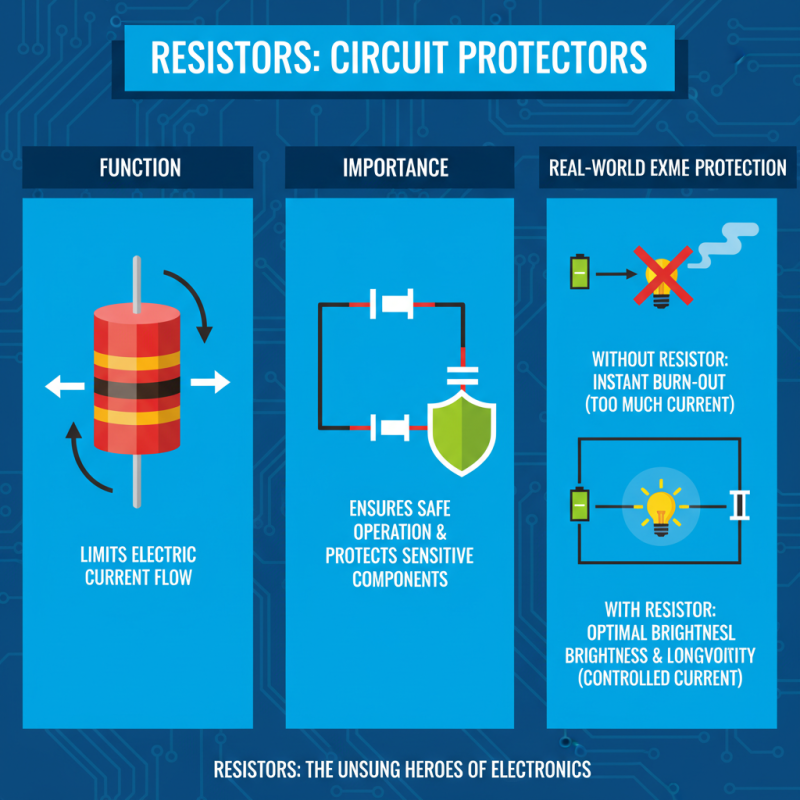
Resistors play a crucial role in electronic circuits. They limit the flow of electric current, ensuring devices operate safely. By introducing resistance, they protect sensitive components from damage. For instance, using the right resistor can prevent overheating in LEDs. Too much current can burn them out instantly.
Understanding resistance helps in circuit design. Ohm's Law connects voltage, current, and resistance. This principle guides engineers in choosing the correct resistors. However, it's easy to make mistakes. If the resistor's value is too high, required current may not flow. This can cause devices to function poorly or not at all.
Resistors come in various types and sizes. Each serves a different purpose, like fixed or variable resistors. Misjudging their role can lead to circuit failure. Therefore, careful consideration when selecting resistors is needed. The impact of these small components is significant, shaping how circuits perform under various conditions.
The Role of Resistors in Current Limiting and Voltage Division
Resistors play a crucial role in electronic circuits. They limit current flow, ensuring components operate safely. For industries, this is vital. A report from the International Electrotechnical Commission highlights that improper current management can lead to failures. Resistors help divide voltage in various applications. This division is essential in designing circuits.
The resistor's function lies in Ohm’s Law. According to this principle, the voltage drop across a resistor is proportional to the current flowing through it. This relationship allows engineers to calculate the necessary resistor values for their circuits. For instance, a circuit requiring 12V may use resistors to ensure components only receive specific voltages.
**Tip:** Always check resistor ratings for power handling. Underrated resistors can overheat, leading to circuit failure.
Capacitors also have indispensable roles in circuits. They store and release energy. This function aids in smoothing power supply fluctuations. Without capacitors, devices could become unstable. However, using the wrong capacitor can cause inefficiencies.
**Tip:** Consider capacitor voltage ratings carefully. Exceeding these can cause failures too.
Finding the right balance between resistors and capacitors is often challenging. Engineers must meticulously analyze circuit requirements. They aim for efficiency while avoiding potential pitfalls.
The Role of Resistors and Capacitors in Electronic Circuits
This chart illustrates the effects of resistors and capacitors in various scenarios, such as current limiting and voltage division in electronic circuits. The data represents the normalized values of voltage across the components in a simple circuit using different resistor values and capacitance levels.
Exploring Capacitors: Definition and Function in Circuits
Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits. They store electrical energy temporarily. This energy can be released when needed. Their ability to charge and discharge makes them vital in various applications.
In simple terms, a capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material. This design enables capacitors to hold a charge. When connected to a voltage source, they fill up with energy. When the circuit calls for energy, the capacitor discharges.
Tips: Always check the capacitor's voltage rating. Using a capacitor rated for a lower voltage can lead to failures. Also, remember that capacitors can take time to discharge fully. Be cautious when handling them.
In circuits, capacitors help smooth out voltage fluctuations. They can filter signals and improve power supply stability. However, not all circuits need capacitors. It can be easy to overlook their necessity in some designs. Balancing component use requires understanding potential trade-offs. Always consider your circuit's specific needs before including them.
How Capacitors Store and Release Electrical Energy
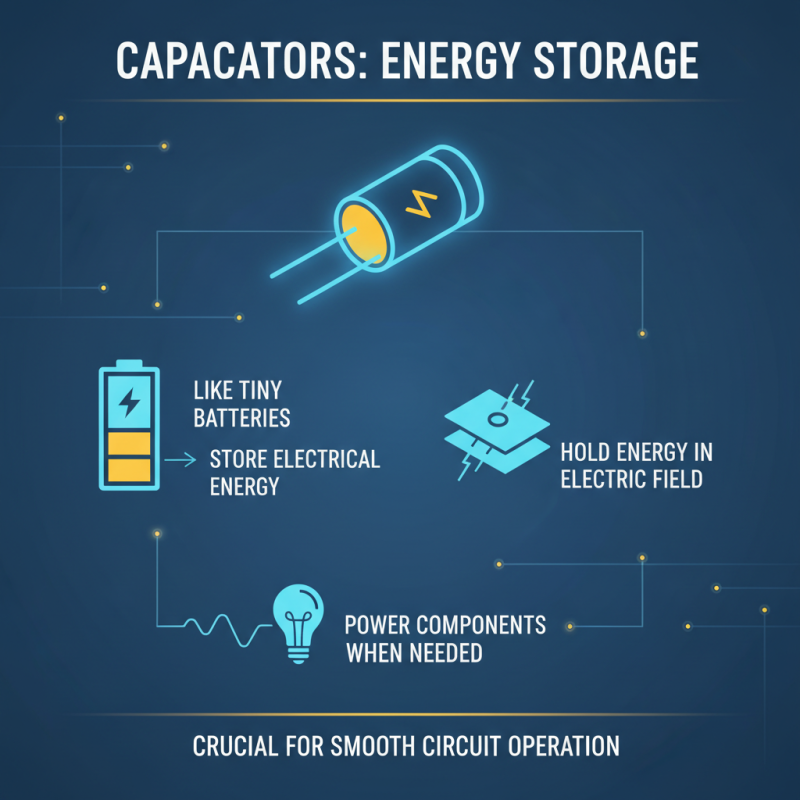
Capacitors are fascinating components in electronic circuits. They store electrical energy, acting like tiny batteries. When charged, they hold energy in an electric field. This stored energy can power other components when needed. It’s crucial for smooth circuit operation.
The process of charging a capacitor begins when voltage is applied. Electrons move to one plate, creating a negative charge. The other plate becomes positively charged. This creates an electric field, allowing energy storage. Capacitors can release this energy rapidly. For instance, they help stabilize power supply fluctuations.
However, not all capacitors function perfectly in every circuit. Some may have leakage issues or reduced capacity over time. These imperfections can lead to unexpected circuit behavior. Understanding these limitations is vital for effective circuit design. Experimentation and observation can lead to better outcomes.
Interplay Between Resistors and Capacitors in Timing Applications
Resistors and capacitors play pivotal roles in electronic circuits, especially in timing applications. The interaction between these two components creates predictable delays or oscillations. For instance, when a capacitor charges through a resistor, it affects the timing of the output voltage. The RC time constant defines how quickly a capacitor can charge. This relationship is crucial in circuits like timers and oscillators.
In many applications, designers must choose precise values for resistors and capacitors. The wrong value can lead to inaccurate timing. Imagine a blinking LED that should pulse every second. If the resistor is too high or the capacitor too low, the timing will be off. It’s sometimes tricky to get the right balance. Different applications can change requirements significantly, demanding a keen eye for detail.
Testing the circuit is vital to ensure accuracy. Sometimes, the theoretical values do not match real-world results. Environmental factors can alter performance as well. Variations in temperature can impact resistance, while capacitor leakage can affect charge times. Adjustments may be needed to refine the timing. The interplay between resistors and capacitors is both an art and a science. It requires careful consideration and continuous experimentation.
What is the Role of Resistors and Capacitors in Electronic Circuits? - Interplay Between Resistors and Capacitors in Timing Applications
| Component | Symbol | Function | Example Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | R | Limits current flow and drops voltage | 1kΩ, 10kΩ, 100kΩ |
| Capacitor | C | Stores and releases electrical energy | 1μF, 10μF, 100μF |
| Stack Application | R-C Circuit | Used for filtering signals and timing applications | R = 10kΩ, C = 10μF |
Related Posts
-
How to Optimize Electronic Resistors for Improved Circuit Performance and Reliability
-

The Hidden Importance of Active Components in Everyday Products
-

Why Electronics Products are Essential for Modern Living and How to Choose the Best Ones
-
How to Choose the Right Resistors and Capacitors for Your Electronics Projects
-
Top Electronics Products to Watch in 2025 Trends and Innovations You Need to Know
-
Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Electronic Capacitors for Your Projects
