News / Blog
How to Select the Right Passive Components for Your Electronic Projects
Selecting the right passive components is a crucial step in the design and execution of electronic projects. These components, which include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, play vital roles in the functioning of electronic circuits. Understanding the specifications and characteristics of each type is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. As electronic devices become more advanced and intricate, the need for appropriate passive components grows, making it imperative for engineers and hobbyists alike to have a solid grasp of their options.
When embarking on an electronic project, considering the specific requirements of the design, such as voltage levels, current flows, and frequency responses, can significantly influence the choice of passive components. Additionally, selecting components that align with the project's budget and performance requirements can help avoid costly mistakes and inefficiencies down the line. Thus, it is beneficial to not only familiarize oneself with the different types of passive components available but also to develop a systematic approach to their selection, ensuring that every component functions harmoniously within the overall circuit.
In conclusion, understanding how to select the right passive components is essential for anyone involved in electronic design. With the right knowledge and tools, project designers can maximize the efficiency of their circuits, leading to successful outcomes. This guide aims to equip you with the insights needed to make informed decisions when incorporating passive components into your electronic projects.
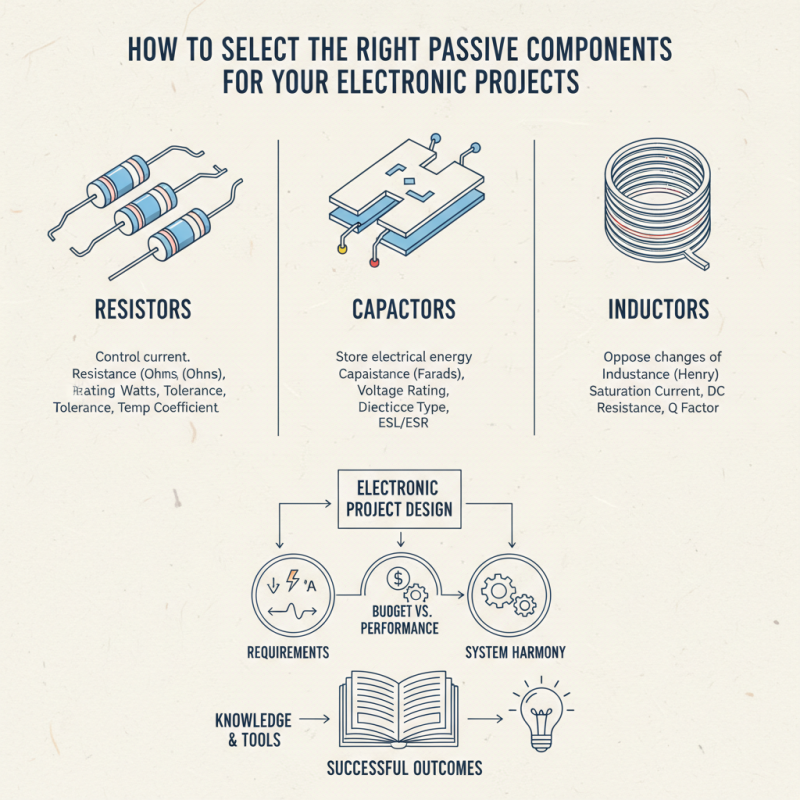
Understanding the Role of Passive Components in Electronic Circuits

Passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, play a crucial role in shaping the behavior of electronic circuits. Unlike active components, passive devices do not provide gain or power; instead, they operate by consuming, storing, or dissipating energy. Resistors limit current flow, capacitors store energy in an electric field, while inductors store energy in a magnetic field. The interplay between these components is vital for ensuring circuit stability and performance, making them indispensable in everything from simple hobby projects to complex industrial applications.
According to a report by the Industry Research Institute, the global market for passive electronic components is expected to reach $50 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics, automotive applications, and renewable energy technologies. For instance, capacitors are essential in filtering applications and power supply circuits, which are projected to grow significantly as industries move towards more energy-efficient designs. Understanding the specifications and characteristics of these passive elements, such as tolerance levels, temperature coefficients, and voltage ratings, is vital for engineers and hobbyists alike. Proper selection ensures reliability and performance, significantly affecting the functionality of the entire circuit.
Key Parameters to Consider When Selecting Capacitors and Resistors
When selecting capacitors and resistors for your electronic projects, there are several key parameters to consider that can significantly affect the performance of your circuit. For capacitors, the capacitance value is crucial, as it determines the amount of charge the component can store. Additionally, the voltage rating of a capacitor must exceed the maximum voltage it will experience in the circuit to prevent breakdown. Another important factor is the equivalent series resistance (ESR), which affects the efficiency and thermal performance of the capacitor. The choice of dielectric material can also influence characteristics such as temperature stability and frequency response, which are important in applications involving signal processing.
On the other hand, for resistors, the resistance value is the primary consideration, as it dictates the current flow in your circuit. The temperature coefficient is another critical parameter, as it indicates how much the resistance will change with temperature variations. For projects requiring precision, tolerance ratings become essential, as they specify how much the actual resistance can deviate from the stated value. Power rating is also a key factor, ensuring that the resistor can handle the power dissipation without overheating. By carefully evaluating these parameters, you can select the most appropriate passive components that will enhance the reliability and efficiency of your electronic designs.
Comparing Inductor Types and Their Applications in Circuit Design
When designing electronic circuits, selecting the right inductor type is crucial for achieving optimal performance. Inductors play a vital role in filtering, energy storage, and voltage regulation. Two common types of inductors are air-core and ferrite-core inductors. Air-core inductors are often preferred for high-frequency applications due to their linear inductance characteristics and lower losses, which make them ideal for RF circuits. However, they can be bulkier and less efficient in low-frequency applications.
On the other hand, ferrite-core inductors exhibit higher inductance values in a smaller footprint, making them well-suited for power supply circuits and low-frequency applications. They provide better attenuation of high-frequency noise, which is essential in maintaining the integrity of sensitive signals. Additionally, the selection between shielded and unshielded ferrite-core inductors can impact performance significantly, especially in terms of electromagnetic interference (EMI) management. By understanding the characteristics and applications of different inductor types, designers can make informed decisions that enhance the functionality and efficiency of their electronic projects.
How to Select the Right Passive Components for Your Electronic Projects - Comparing Inductor Types and Their Applications in Circuit Design
| Inductor Type | Inductance Range (µH) | Current Rating (A) | Application Areas | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Inductor | 1 - 1000 | 0.1 - 10 | High-frequency circuits | Compact size, low DC resistance |
| Wirewound Inductor | 10 - 2000 | 0.5 - 50 | Power electronics, filters | High inductance values, stable performance |
| Ferrite Core Inductor | 1 - 1500 | 0.2 - 20 | Switching power supplies, RF applications | High efficiency, good balance of inductance and size |
| Choke Inductor | 10 - 5000 | 0.5 - 100 | Power filtering, EMI suppression | Effective in reducing noise, robust construction |
Evaluating Tolerances and Ratings for Reliable Component Selection
When selecting passive components for electronic projects, evaluating their tolerances and ratings is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance. Tolerances define the acceptable deviation from the specified value, which can significantly impact circuit functionality. For instance, a capacitor with a tolerance of ±10% may result in a significant variance in capacitance, affecting the timing in oscillator circuits. In contrast, tight tolerance components (±1% or better) are essential for precision applications, such as in medical devices or high-frequency communication systems, where performance consistency is vital. According to recent industry reports, around 60% of failures in electronic systems can be attributed to inadequate component selection, emphasizing the importance of meticulous evaluation.
In addition to tolerances, assessing the ratings of passive components—such as voltage, current, and power ratings—is equally important. Each component must be able to handle the electrical stress it will experience in the actual circuit conditions. For instance, resistors operating at values near their rated power can lead to thermal runaway, leading to premature failure. A study conducted by the Electrotechnical Commission revealed that using components within 75% of their rated capacity can enhance reliability by up to 30%. Thus, through careful consideration of tolerances and ratings, engineers can ensure their designs not only meet specifications but also achieve higher longevity and stability in real-world applications.
How to Select the Right Passive Components for Your Electronic Projects
This chart illustrates the importance of various tolerances and ratings for passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors affecting their reliability in electronic projects.
Best Practices for Sourcing Quality Passive Components for Projects
When embarking on electronic projects, selecting quality passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance. Sourcing these components requires a comprehensive understanding of their specifications, tolerances, and the environmental conditions under which they will operate. According to a report published by Industry Research, the global market for passive components is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, highlighting the increasing demand for these critical elements in electronics.
To ensure the quality of passive components, it is essential to establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers and manufacturers. A study by Smithers Pira indicates that about 30% of component failures in electronic devices can be attributed to subpar materials. Thus, implementing best practices such as performing thorough supplier audits, requesting component datasheets, and analyzing previous customer reviews can significantly minimize the risk of sourcing defective parts. In particular, considering components that meet industry standards, such as ISO 9001 certifications, can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
Additionally, leveraging technology for component sourcing has transformed the procurement process. Online platforms allow for real-time comparisons of prices and specifications, enabling engineers to make informed decisions efficiently. Data from Electronics Weekly suggests that about 50% of engineers now utilize online resources to source components, further emphasizing the importance of digital tools in modern procurement strategies. By focusing on these best practices, you can enhance the integrity of your electronic projects and ensure long-term performance of passive components.
Related Posts
-
How to Navigate the Best Electronic Components Website for Your Project Needs
-

Why Electronic Capacitors Are Essential for Modern Electronics
-

The Hidden Importance of Active Components in Everyday Products
-
Exploring Market Trends for Electronic Components at the 2025 Canton Fair in China
-

Top 5 Electronics Supply Sources for Your Next Big Project
-

Why Understanding Electric Switches is Essential for Modern Homes
