News / Blog
Top Passive Components You Need to Know for Your Electronics Projects
In the realm of electronics, understanding the various components that comprise a circuit is crucial for success in any project. Among these components, passive components play a vital role, serving as the backbone of circuit functionality without the need for an external power source. These elements, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, are integral to controlling signals and managing energy within a circuit. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them essential for both beginners and seasoned engineers.
As we delve into the top passive components every electronics enthusiast should familiarize themselves with, we will explore their unique functions and applications. Each of these components contributes to overall circuit performance, whether it’s through filtering signals, regulating voltage, or storing energy. By gaining a deeper knowledge of passive components, you will significantly enhance your ability to design and troubleshoot electronic systems.
This guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of the most essential passive components, illustrating how they can be effectively utilized in various projects. Understanding these components will not only elevate your electronics skills but also empower you to innovate and create with confidence. Let’s embark on this journey to discover the fundamental passive components that can elevate your electronics projects to the next level.
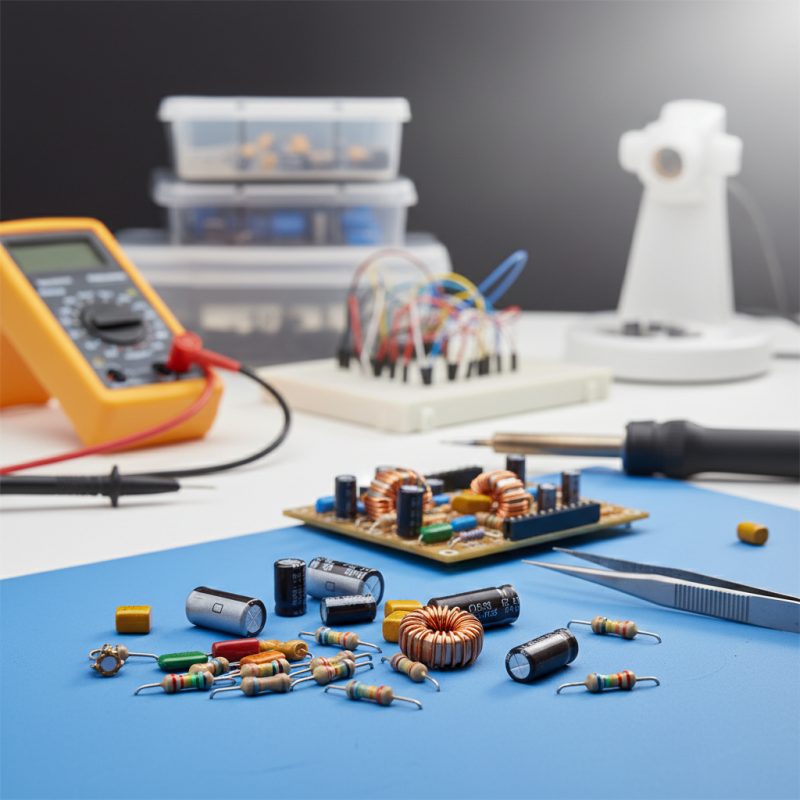

Understanding the Basics of Passive Components in Electronics
Passive components are essential building blocks in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in various applications. Understanding the basics of these components can significantly enhance your ability to design and troubleshoot electronics projects. Key passive components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, each serving a unique function. Resistors limit current flow, capacitors store and release energy, and inductors store energy in a magnetic field. Familiarizing yourself with these components and their characteristics is vital for successful project execution.
**Tips:** When selecting passive components, always check their specifications, such as tolerance values and voltage ratings. This will help you avoid potential circuit failures that could stem from using inappropriate components. Additionally, consider the application to determine whether you need specialized components, like variable resistors or ceramic capacitors, which can offer greater flexibility in your designs.
As you delve into your electronics projects, remember that passive components often work in tandem with active components. Understanding how these parts interact will allow you to optimize circuit performance and efficiency. The integration of various passive components, such as using capacitors in combination with resistors for filtering applications, can lead to more complex and functional circuit designs.
Common Types of Passive Components: Capacitors, Resistors, and Inductors
Passive components play a crucial role in electronic circuits, serving essential functions without requiring an external power source. Among the most common types are capacitors, resistors, and inductors, each contributing uniquely to circuit behavior. Capacitors store and release electrical energy, making them vital for filtering applications and energy smoothing in power supplies. They vary in capacity and voltage ratings, with form factors ranging from tiny surface-mount devices to larger electrolytic types used in bulk energy storage.
Resistors are perhaps the most ubiquitous passive components, controlling current flow and voltage levels in circuits. They come in various forms, such as fixed, variable, and specialty resistors, allowing designers to create circuit conditions that suit their needs. Understanding resistance value, tolerance, and power rating is essential for ensuring they perform as intended in any project.
Inductors, the third key type, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through them. They are primarily used in filtering applications, where they can smooth out electrical signals or separate different frequency components. The selection of inductors involves considering factors like inductance value, current rating, and core material, which directly influence their performance in the circuit. Together, these passive components form the backbone of electronics, enabling engineers and hobbyists to build functional and reliable devices.
Choosing the Right Passive Components for Your Electronics Projects
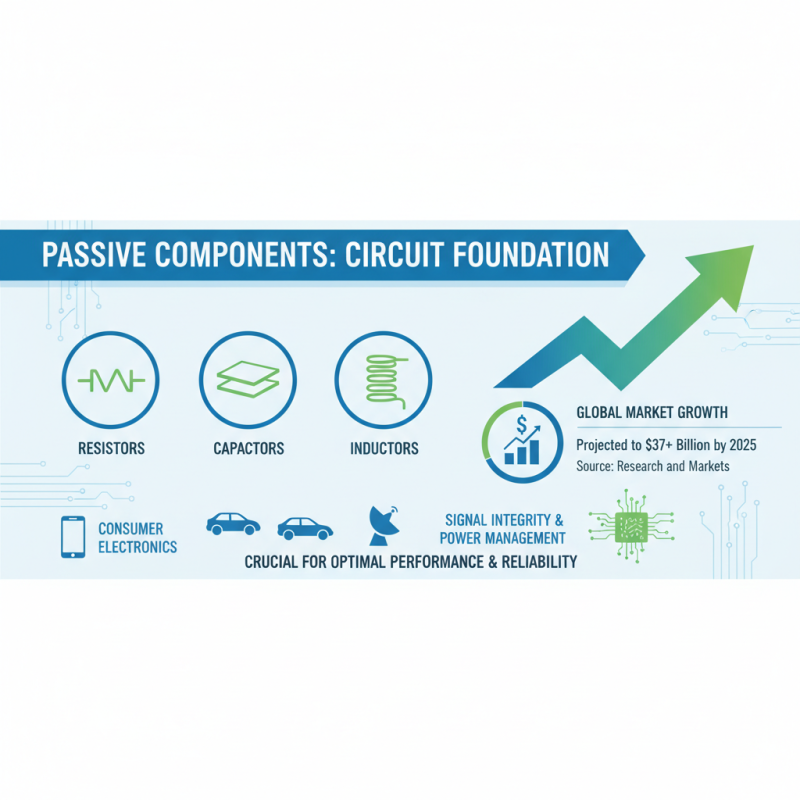
When embarking on electronics projects, selecting the right passive components is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors play a fundamental role in circuit design, affecting everything from signal integrity to power management. According to a recent industry report by Research and Markets, the global passive components market is projected to grow to over $37 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for these essential components in various applications, including consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications.
To choose the right passive components for your projects, it’s important to understand the specific requirements of your application. For instance, the tolerance and power rating of resistors can significantly impact circuit behavior; a report from the Electronic Components Industry Association (ECIA) emphasizes that selecting resistors with appropriate ratings can reduce failure rates by as much as 30%. Similarly, understanding the types and values of capacitors is vital, especially in timing and filtering applications. In fact, a study published in the Journal of Electronic Materials indicates that using high-quality capacitors can improve circuit efficiency by nearly 20%, showcasing the importance of informed choices in component selection.
How Passive Components Influence Circuit Performance and Stability
Passive components play a crucial role in determining the performance and stability of electronic circuits. These components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not amplify electric signals but instead store energy, dissipate it, or filter frequencies. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global passive components market is expected to reach $37.1 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing importance of these elements in various applications, from consumer electronics to telecommunications.
The influence of passive components on circuit performance is profound. For instance, capacitors can store and release energy efficiently, which can smooth out voltage fluctuations, ultimately enhancing the reliability of the circuit. Furthermore, the selection of resistor values can significantly impact power dissipation and heat generation; improper choices can lead to circuit instability. A study published in the Journal of Electronic Materials noted that circuits designed with optimal passive components exhibited a 30% reduction in failure rates under normal operating conditions.
Tip: When designing with passive components, consider the temperature coefficient of resistors and capacitors to ensure stable performance across varying environmental conditions. Additionally, maintaining a balance between quality and cost can improve your project’s overall effectiveness without breaking the budget.
Top Passive Components You Need to Know for Your Electronics Projects
| Component Type | Function | Impact on Circuit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | Limit current flow and divide voltage | Stabilizes voltage levels and prevents overloads | Voltage dividers, biasing |
| Capacitor | Store and release electrical energy | Filters noise, stabilizes voltage, and couples signals | Power supply smoothing, timing circuits |
| Inductor | Store energy in a magnetic field | Filters signals, prevents current spikes | Switching power supplies, RF applications |
| Diode | Allow current to flow in one direction | Protects circuits from reverse polarity | Rectifiers, clamping circuits |
| Ferrite Bead | Suppress high frequency noise | Improves signal integrity, prevents interference | Power supply inputs, data lines |
Best Practices for Integrating Passive Components in Designs
When designing electronic circuits, integrating passive components effectively is crucial for optimal performance. Passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors do not require an external power source and are essential in filtering, timing, and energy storage. According to a report by the Global Passive Component Market Analysis (2023), the demand for passive components is projected to grow steadily, with a significant rise in applications across the automotive and telecommunications sectors, highlighting the importance of mastering their integration.
One best practice for integrating passive components is to carefully consider the placement on your PCB layout. Components should be placed to minimize the length of the connecting traces, which can reduce parasitic inductance and resistance. Furthermore, keeping sensitive analog components away from noisy digital signals can help maintain signal integrity. Employing simulation tools can provide valuable insights into how passive components affect the overall circuit performance, allowing designers to make informed decisions early in the design process.
**Tip**: Always check the tolerances of your passive components. Variations can greatly affect circuit behavior, particularly in precision applications. Aim for tight tolerances when precision is critical, especially in feedback loops. Additionally, implement capacitors with a voltage rating that exceeds the expected operating conditions by at least 20% to ensure reliability and performance. Regularly reviewing the latest performance metrics in industry reports can help designers stay ahead of emerging trends and best practices.
Related Posts
-
How to Select the Right Passive Components for Your Electronic Projects
-
Top Websites for Buying Electronic Components Online Easily and Affordably
-

Top 10 Electric Switches for Smart Homes: Upgrade Your Control Today!
-

Why Electronics Products are Essential for Modern Living and How to Choose the Best Ones
-
Exploring the Future: How Capacitors Can Transform Sensing Technology
-
How to Navigate the Best Electronic Components Website for Your Project Needs
