News / Blog
Top Passive Electronic Components That Every Engineer Should Know?
In the world of electronics, passive electronic components play a critical role. According to Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned expert in electronic engineering, "Understanding passive components is essential for any successful design." These components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. They do not amplify signals but are vital to circuit functionality.
Every engineer should be familiar with these elements. Resistors manage current flow, while capacitors store and release energy. Inductors can filter signals effectively. Yet, many overlook their importance during the design phase. This oversight can lead to inefficient circuits and increased energy consumption.
Engineers must delve deeper into the characteristics of passive electronic components. Incomplete knowledge can lead to design failures. Each component has specific parameters that impact performance. Thus, understanding these components fully is key to innovation in electronics.
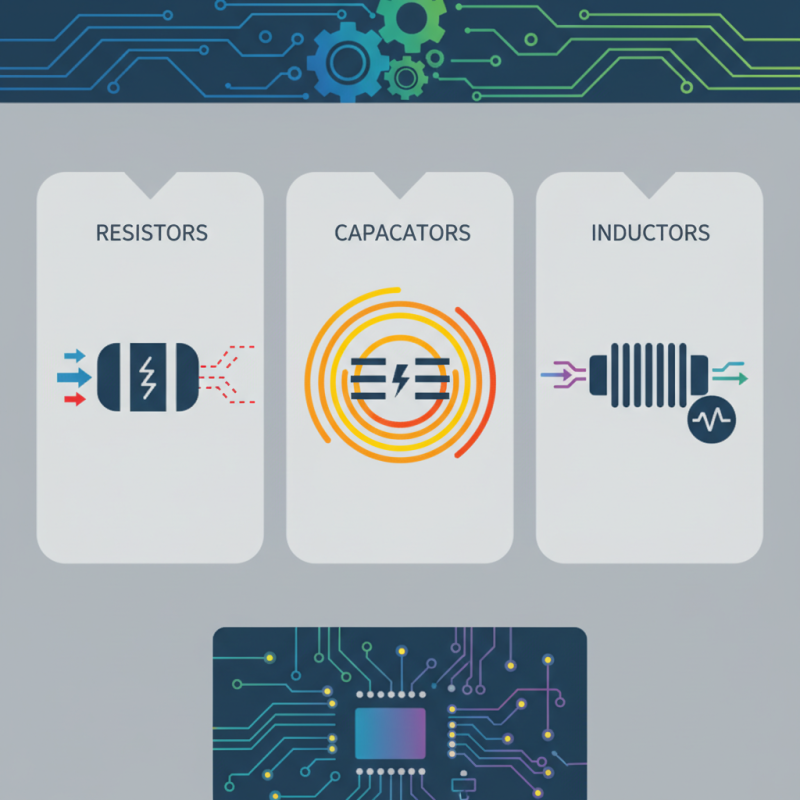
Essential Characteristics of Passive Electronic Components
Passive electronic components play a vital role in circuit design. These components do not generate energy but instead store, dissipate, or control it. They include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. According to recent data, the global passive components market is projected to reach $32 billion by 2027. This highlights their importance in technology.
Resistors limit current flow and divide voltages, critical in circuit stability. Capacitors store energy, smoothing voltage fluctuations. As of 2022, capacitors represented 40% of the passive components market, indicating their widespread application in power systems. Inductors, essential for filtering signals, account for 20% of this market. Their use in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems shows the increasing demand.
Engineers must understand the limitations of these components. For instance, capacitors can fail if voltage ratings are exceeded. Resistors may dissipate heat, causing performance issues. The inconsistency in the manufacturing process can lead to variation in resistance values. These are challenges engineers face regularly. Such factors underline the importance of selecting the right components for optimal performance in designs.
Common Types of Passive Electronic Components Engineers Should Know
Passive electronic components play a crucial role in various circuits. They do not require external power to operate. Instead, they rely on the signals they receive. Here are some common types every engineer should know.
Resistors are the most basic passive components. They limit the flow of electric current. The unit of resistance is ohms. Choosing the right resistor can impact performance. Pay attention to tolerance levels. It can affect circuit behavior too.
Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily. They release it when needed. Capacitors come in various types, such as ceramic and electrolytic. Each type has specific uses. Think about voltage ratings and capacitance value. Always verify specifications.
Inductors are also essential. They store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors resist changes in current flow. This makes them vital in filters and oscillators. Remember, the size and type of inductor affect performance.
Tips: When selecting passive components, consider the entire circuit. A small change in one component can lead to significant differences. Always double-check your calculations and specifications before implementation. Don't rush; mistakes can be costly.
Another tip: prototyping is invaluable. Build test circuits to observe real behavior. Sometimes, theory deviates from practice. Learning from these differences is key to becoming a better engineer. Embrace the trial-and-error process.
Applications of Passive Components in Electronic Circuits
Passive components play a crucial role in the design of electronic circuits. These components, unlike active ones, do not require power for their operation. Resistors, capacitors, and inductors are the primary types. Each has unique properties that make them essential for various applications.
In filtering, capacitors store energy and smooth out voltage fluctuations. They prevent noise from entering circuits. Inductors, on the other hand, store energy in a magnetic field. They are often used in power applications to regulate current flow. Resistors limit current and divide voltages, ensuring that components operate within safe levels. Their applications are diverse, ranging from basic circuit protection to complex filtering systems.
Engineers sometimes underestimate the importance of these components. Choosing the wrong value can lead to circuit failures. Understanding the specifications of passive components is vital. Each component's tolerance and temperature coefficient can impact performance. Small mistakes here can result in significant issues later. It's clear that mastering these components is essential for efficient circuit design.
Top Passive Electronic Components Usage in Applications
Factors Influencing the Selection of Passive Components
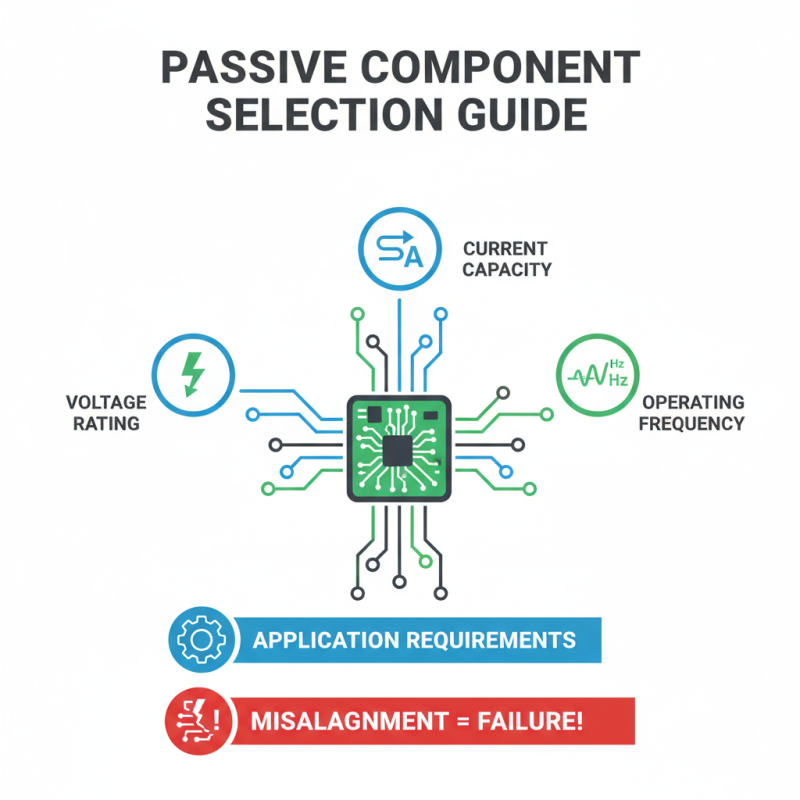
When selecting passive electronic components, several factors come into play. Engineers must consider the specific application requirements. These include voltage ratings, current capacities, and operating frequencies. Each component has unique specifications that affect its performance and reliability. Misalignment between the component and the application can lead to failures. Understanding these details is crucial.
Another key factor is the environmental conditions. Temperature, humidity, and mechanical stress can impact the performance of passive components. Engineers often overlook how these elements influence durability. Choosing components that perform well under varying conditions is essential. In some cases, engineers might prioritize cost over quality. This can lead to regrettable decisions that affect the overall design's longevity.
Choosing materials wisely also matters. Different materials can affect the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors. For example, the dielectric material in capacitors can significantly influence performance. Sometimes, engineers might wish to cut corners, opting for cheaper alternatives. However, this can compromise circuit performance, leading to unexpected issues down the line. The balance between budget constraints and quality requirements is often challenging.
Trends and Innovations in Passive Electronic Component Design
The field of passive electronic components is experiencing dynamic changes. Engineers are embracing new designs that enhance functionality while reducing size. For instance, advancements in capacitor technology now include high-density materials. These materials allow for smaller capacitors that offer greater capacitance. This shift is crucial in compact devices, where space is at a premium.
Another exciting trend is the development of inductors with improved magnetic materials. These materials minimize energy losses and enhance performance. A well-designed inductor can now handle higher frequencies, making it ideal for modern applications. Engineers should also be aware of the growing popularity of integrated resistors. These resistors can significantly reduce PCB space while improving thermal stability.
However, it’s essential to recognize some challenges in this evolving landscape. As components become smaller, the risk of overheating increases. Designers must carefully consider thermal management techniques. The balance between size and performance is often delicate. Engineers need to reflect on these aspects to ensure optimal designs.
Related Posts
-
How to Optimize Electronic Resistors for Improved Circuit Performance and Reliability
-
Exploring the Growth of Passive Electronic Components at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Insights and Opportunities
-
Navigating Trends in Electronic Components at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Electronic Components in Smart Technology Development
-

Top 10 Active Components Driving Innovation in Cosmetic Formulations for 2023
-

What Are Passive Components and How Do They Work in Electronics?
